- Yes
- No
[Boh Koh 17A or B.Kh.17A]
OVERVIEW
The North American F-86D/K/L “Sabre Dog” was a specialized interceptor series derived from the legendary F-86 Sabre, developed for the U.S. Air Force in the late 1940s. While the original F-86 was designed as a high-speed day fighter, the Sabre Dog variants were purpose-built for all-weather interception, featuring major structural and systems changes. These included a larger fuselage, a powerful afterburning engine (J47-GE-17B or -33), and a distinctive nose radome housing an onboard radar and fire control system. Armament also differed significantly—replacing guns with a retractable tray carrying 24 × 2.75-inch “Mighty Mouse” folding-fin aerial rockets.

F-86D with ‘Mighty Mouse’ FFAR rocket tray
The F-86L specifically emerged as an upgraded version of the F-86D under “Project Follow-On.” Its primary enhancement was the integration of the AN/ARR-39 datalink for compatibility with the revolutionary SAGE (Semi-Automatic Ground Environment) system. SAGE, developed by MIT’s Lincoln Laboratory and introduced in 1953, was one of the most advanced military computing systems of its time. It enabled ground-based radar stations to process tracking data and automatically relay real-time interception vectors to the pilot, guiding the aircraft toward its target. This system significantly reduced pilot workload and communication errors that plagued earlier ground-controlled intercept methods.

Electronics found in an F-86L
All F-86Ls were conversions of low-hour F-86Ds, brought up to F-86D-45 standards before being outfitted with upgraded avionics. These included the AN/ARC-34 radio, AN/APX-25 IFF transponder, AN/ARN-31 glide slope receiver, and new cooling ducts on the fuselage sides. The most significant airframe change was the adoption of the F-86F-40 wing, featuring 12-inch extended wingtips and leading-edge slats, increasing wingspan to 39.1 feet and wing area to 313.37 square feet. This modification improved high-altitude handling and turn performance.
Taken from: 2003, Curtis, D., North American Sabre Dog, pt. 3 - ANG & Foreign F-86D,K,L (Air Force Legends 211)
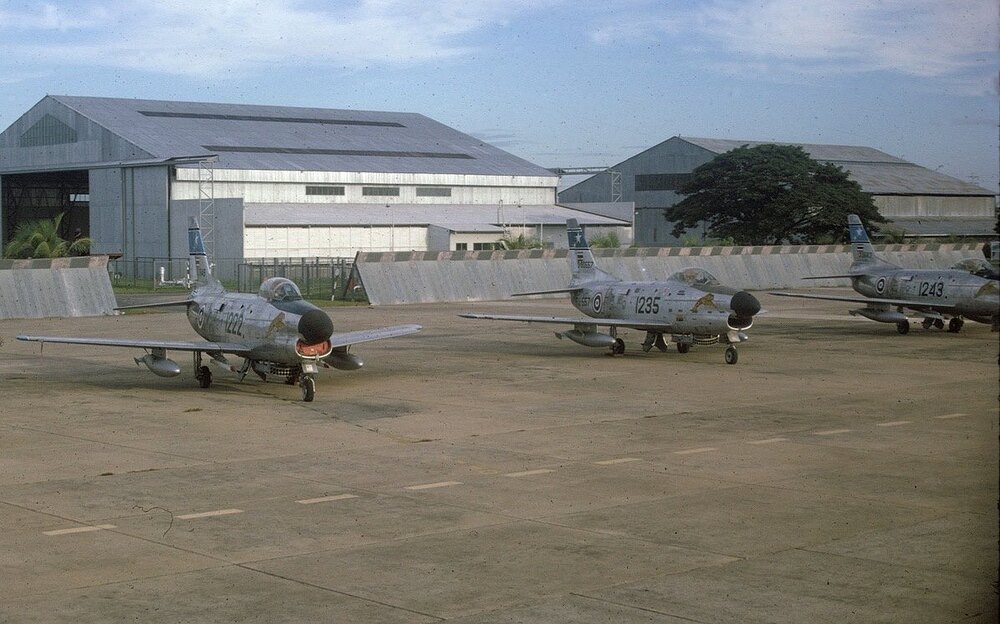
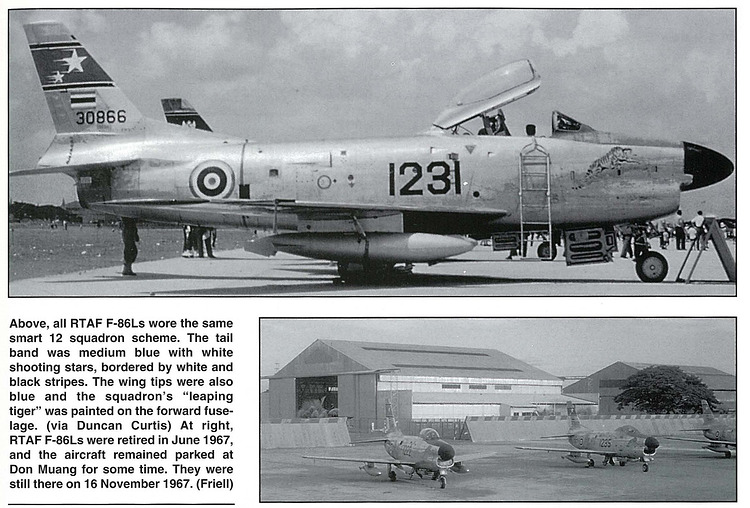
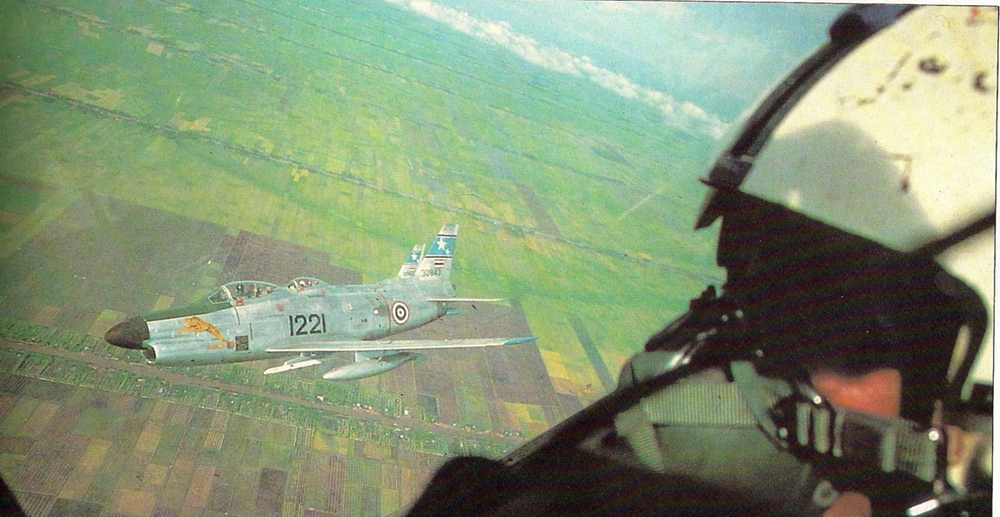
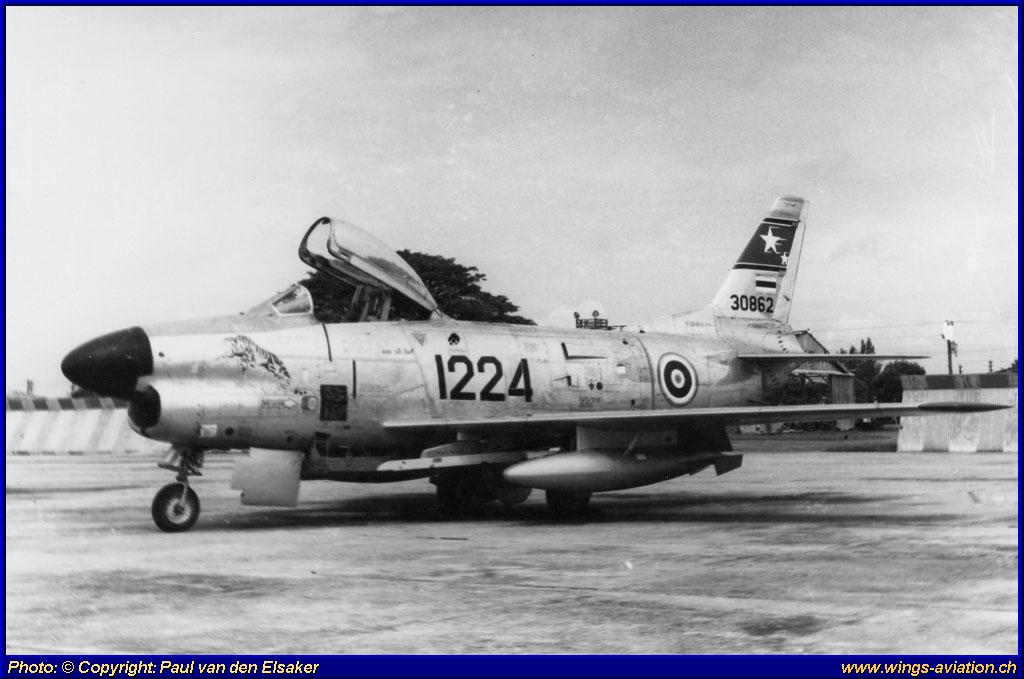
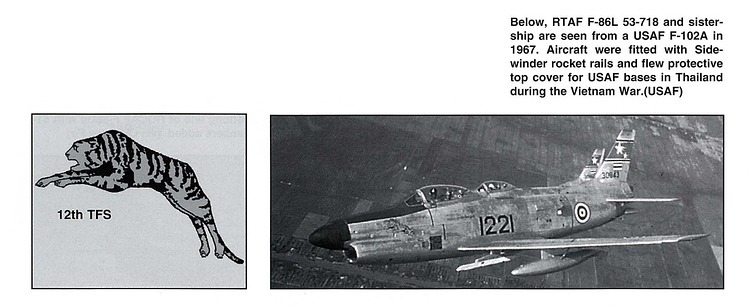
Under the Military Assistance Program (MAP) in the early 1960s, a number of surplus F-86L aircraft were transferred to allied air forces, including the Royal Thai Air Force. Thailand received approximately 20 F-86Ls, using them in the air defense role. However, due to the absence of a supporting SAGE network in Southeast Asia and the aircraft’s demanding upkeep, their service life in Thailand was short. By the late 1960s, most Thai F-86Ls were retired, marking a brief but important phase in the modernization of Thailand’s Cold War-era air defense capabilities.
Under its service with the Royal Thai Air Force, the F-86L was fitted with rails for the AIM-9B Sidewinder to better suit the RTAF’s needs similar to what can be found with its F-86F Sabres. They served under the 12 Tactical Fighter Squadron based on Don Muang, Thailand and flew protective top cover for USAF bases during the Vietnam War. They were replaced with proper COIN aircraft to better suit the Counter-Insurgency Operations that Thailand actually faced and not interceptors.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | All-weather Interceptor |
| Manufacturer | North American Aviation |
| Crew | 1 (pilot) |
| Powerplant | 1 × General Electric J47-GE-33 turbojet with afterburner |
| Thrust | 5,425 lbf (24.1 kN) dry / 7,500 lbf (33.4 kN) with afterburner |
| Maximum Speed | Approx. 692 mph (1,114 km/h) at sea level |
| Range | 800 mi (1,287 km) combat radius |
| Service Ceiling | 49,750 ft (15,160 m) |
| Rate of Climb | 12,000 ft/min (3,660 m/min) |
| Length | 40 ft 4 in (12.29 m) |
| Wingspan | 39 ft 1 in (11.91 m) with F-40 extended slatted wings |
| Height | 15 ft 0 in (4.57 m) |
| Wing Area | 313.37 sq ft (29.11 m²) |
| Empty Weight | Approx. 13,000 lb (5,897 kg) |
| Loaded Weight | 16,292 lb (7,390 kg) |
| Max Takeoff Weight | 19,975 lb (9,061 kg) |
| Armament | 24 × 2.75 in (70 mm) FFAR “Mighty Mouse” rockets in retractable tray |
| 2 × AIM-9B Sidewinder air-to-air missiles (underwing) | |
| Avionics | Hughes E-4 fire control system, AN/ARR-39 SAGE datalink receiver, AN/APX-25 IFF, AN/ARN-31 glide slope receiver |
| Notable Features | Extended slatted wing (F-40), drag chute, SAGE-compatible interception guidance system |

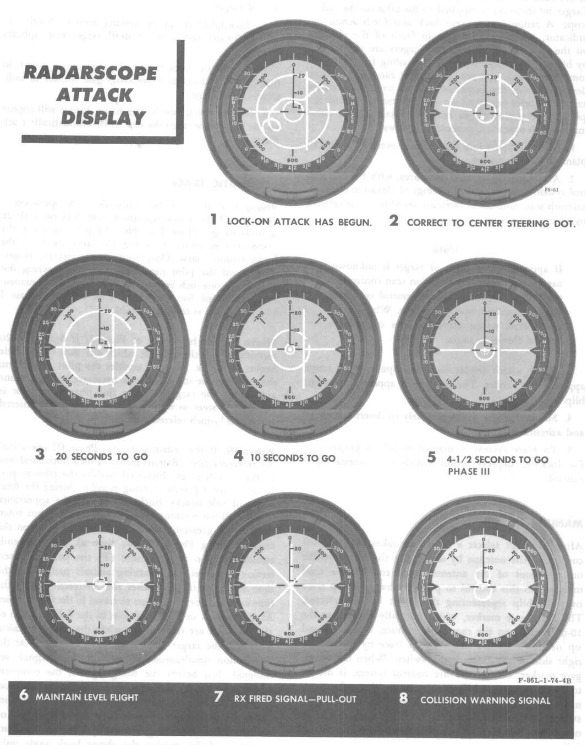
The F-86L has a Fire Control Radar to tell you when to shoot the FFAR rockets
IN-GAME
Similar to the F-86K found in the German Tech Tree, I propose this to be at a 9.0 - 9.3 BR but as discussed earlier, it will not have guns but instead have air-to-air rockets as its primary armament instead.
This would be a good alternative to the Japanese F-86D that is yet to be added, and compared to that - this has significantly better value for the game mechanics of War Thunder since it has AIM-9Bs to rely on after you expend the 24 rockets you have. Keep in mind the rockets have an FCS system so you can try to be accurate with them.

The JASDF F-86D does not have AIM-9Bs
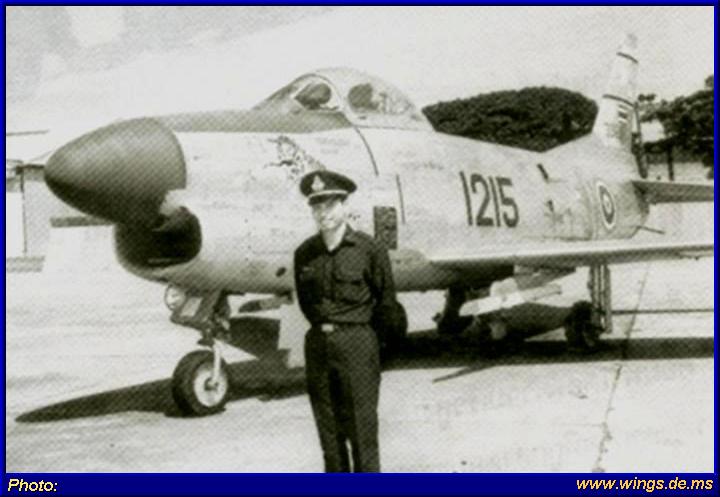
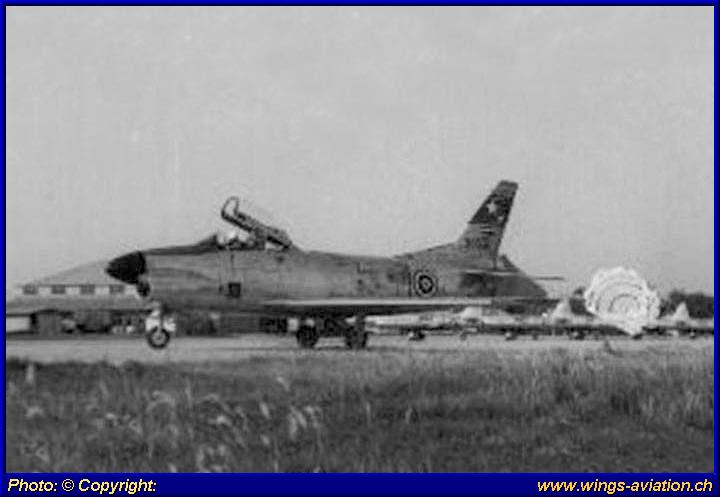
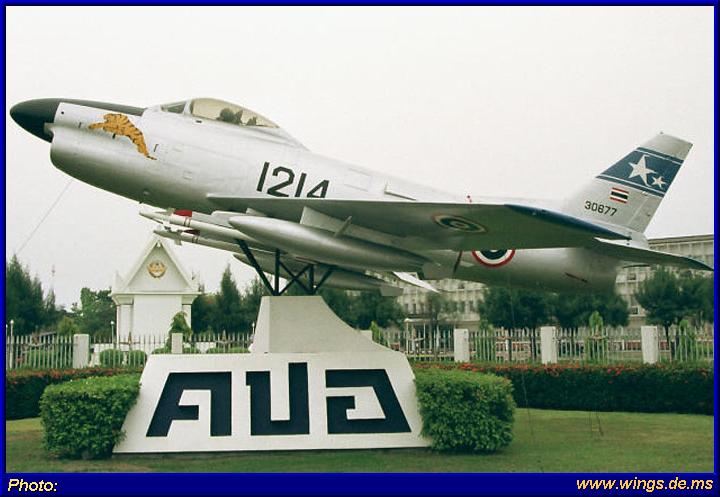
MORE PHOTOS




SOURCES
Special Thanks to @Disco_Shrimp for his excellently written F-86L ‘Sabre Dog’ proposal for the American Tech Tree and to @MapleVII-live for his similare F-86D proposal for the Chinese Tech Tree - please do check them out!
Curtis, D. (2003). North American Sabre Dog, pt. 2 – USAF F-86D, L (Air Force Legends 207). Ginter Books.
U.S. Air Force. (1961, July). T.O. 1F-86L-1 Flight Handbook: USAF Series F‑86L aircraft [PDF]. DocDroid. North American F-86L Flight Handbook.pdf | DocDroid
Allward, Maurice. F-86 Sabre. London: Ian Allan, 1978. ISBN 0-7110-0860-4.
http://www.wings-aviation.ch/11-RTAF/2-Aircraft/NorthAmerican-F-86/Sabre.html
https://www.scramble.nl/planning/orbats/thailand/royal-thai-air-force-history
https://www.airvectors.net/avf86_2.html
Special Hobby 1/72 F-86L Sabre, previewed by Scott Van Aken.