Would you like to see T-55AMV in-game?
- Yes, as a Tech-Tree Vehicle
- Yes, as a Premium Vehicle
- Yes, as a Squadron Vehicle
- Yes, as an Event Vehicle
- No, I do not want to see T-55AMV in-game.
0
voters
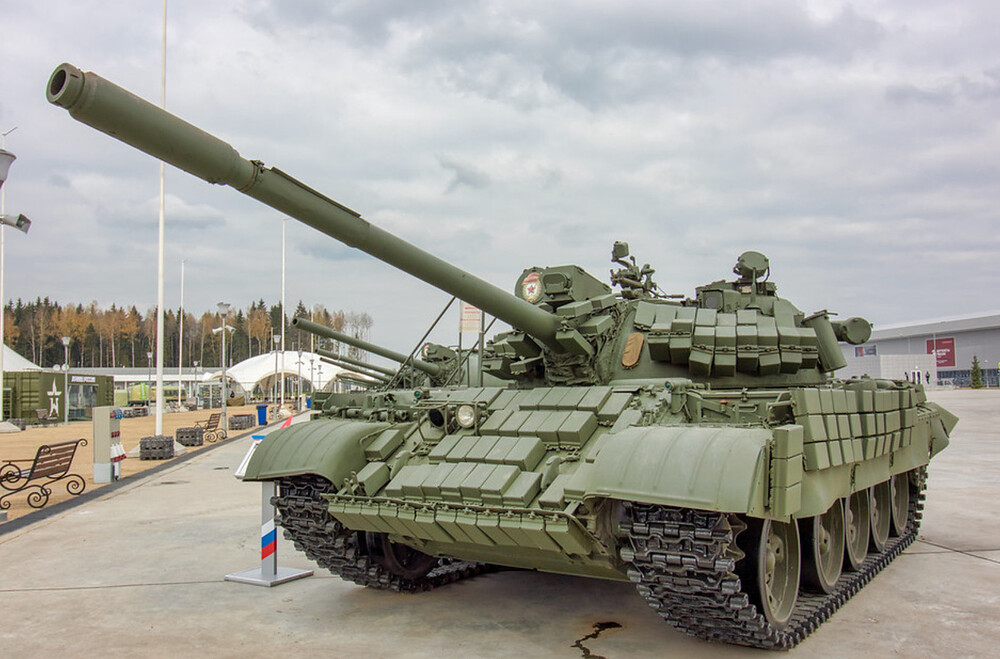
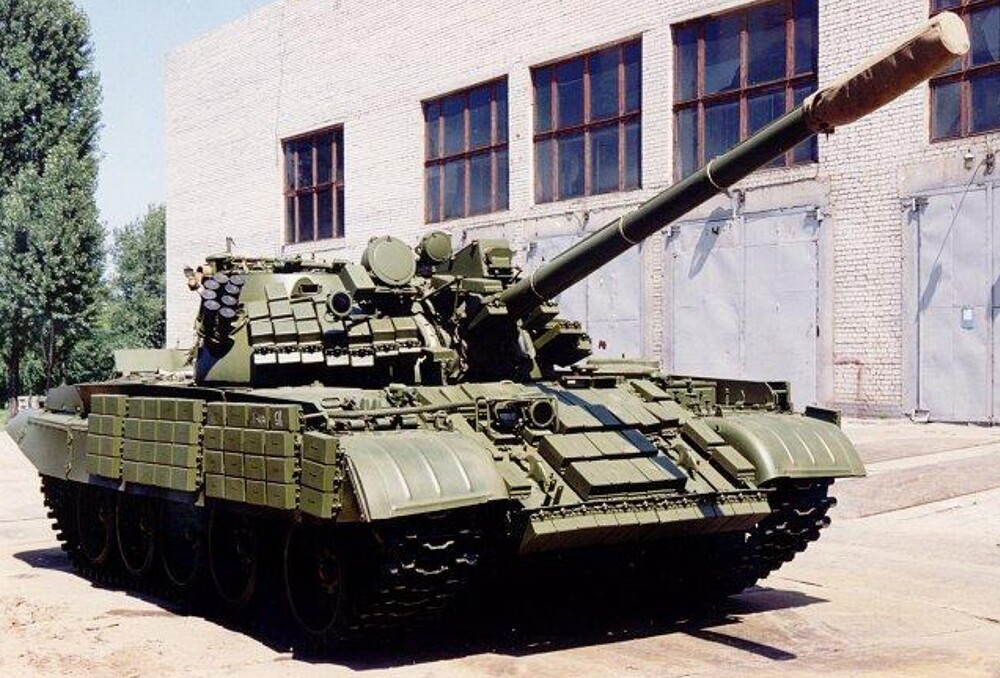
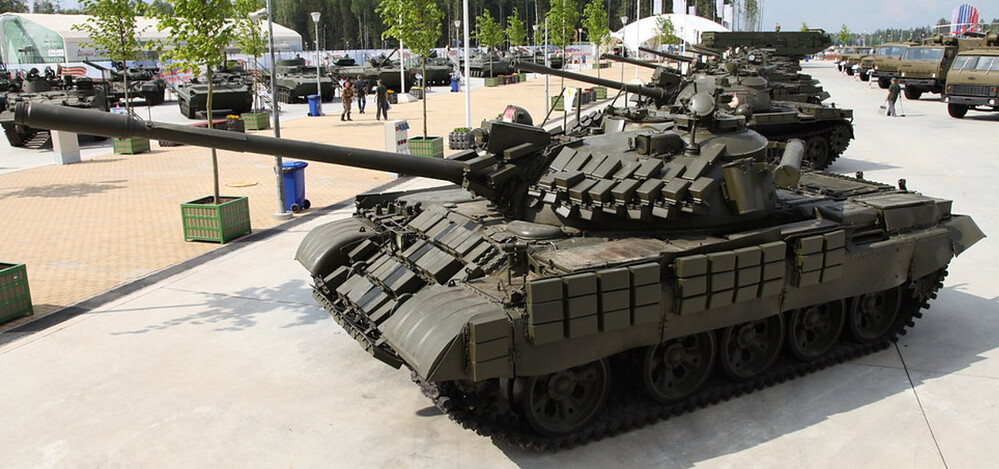
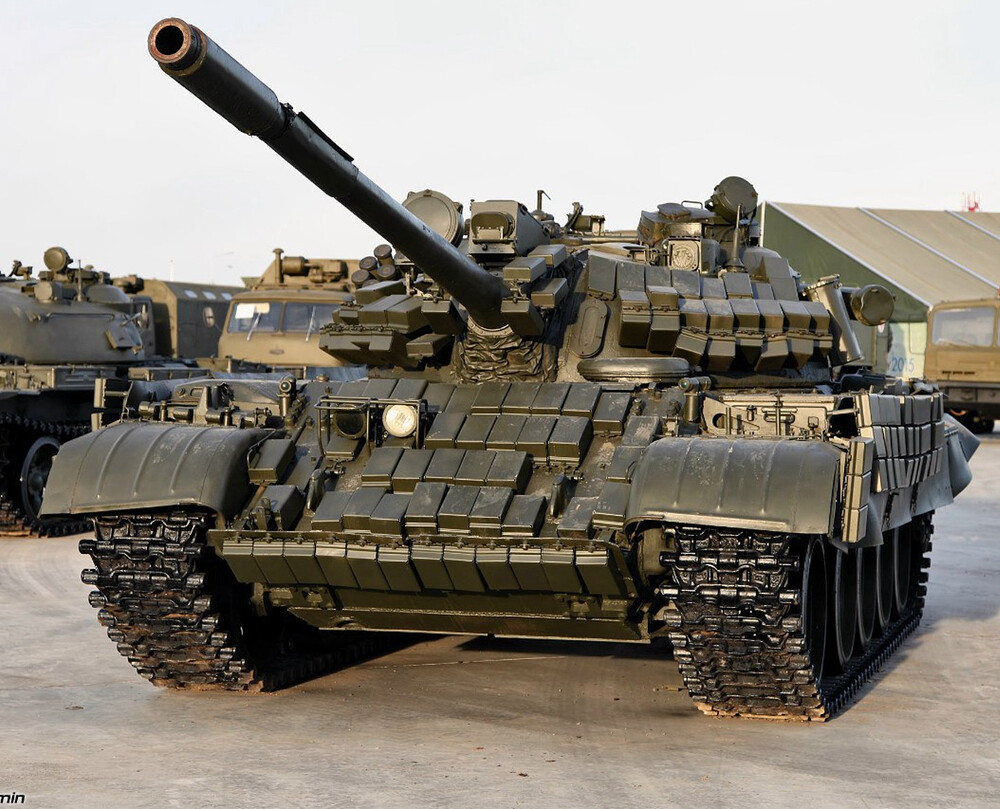
T-55AMV – Battle-Tested, Globally Trusted
Introduction
The T-55AMV is an advanced upgrade of the Soviet T-55 tank, introduced in the mid-to-late 1980s as part of an effort to extend the battlefield relevance of older armor platforms. Developed in response to lessons learned from conflicts like the war in Afghanistan, the upgrade aimed to bring the aging T-55 up to more modern standards in terms of protection, firepower, and electronics, while maintaining affordability and leveraging existing chassis. The AMV variant built upon earlier upgrades like the T-55AM by integrating lighter Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armor (ERA) into the protection suite, replacing passive armor enhancements on the turret. The “V” designation refers specifically to the implementation of Kontak-1 ERA blocks. Just like the T-62MV, the purpose of the T-55AMV was to counter armed formations relying on shaped-charge anti-tank weaponry, whereas the T-62M and T-55AM were primarily designed to address kinetic threats.
Brief History: From T-55 to T-55AMV
Spoiler
The T-55 was introduced by the Soviet Union in the late 1950s as an evolution of the T-54, and it quickly became one of the most widely produced and exported tanks in history. Its design emphasized simplicity, reliability, and ease of mass production, making it an ideal platform for both Soviet use and international allies. While well-suited for its time, the T-55’s capabilities began to fall behind by the 1970s as new anti-tank threats, such as HEAT warheads and more powerful Western tank guns, proliferated on the battlefield.
To extend the life of the aging T-55 fleet, the Soviet Union initiated several modernization programs. The first major effort came in the late 1970s and early 1980s, leading to the T-55M and T-55AM variants. These upgrades introduced new fire control systems, a laser rangefinder, a ballistic computer, improved night-fighting optics, and the ability to fire the 9M117 gun-launched ATGM through the standard 100 mm cannon. Protection was also enhanced through the addition of composite applique armor on the turret and hull.
The T-55AMV followed soon after as a refinement of the AM package, replacing the bulky passive armor with Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armor. This made the modernization cheaper and the tank more effective against shaped-charge weapons such as RPGs and ATGMs. The AMV variant retained all other improvements from the AM model but focused primarily on raising protection to meet the evolving threats of asymmetric warfare and low-intensity conflicts. While the AMV did not see widespread use in the Soviet Army, it became a popular export option, especially for countries seeking affordable yet capable upgrades to existing T-55 fleets. Its success overseas cemented the T-55AMV as a practical example of how an aging Cold War design could remain effective well into the 21st century.
Armor and Protection
Spoiler
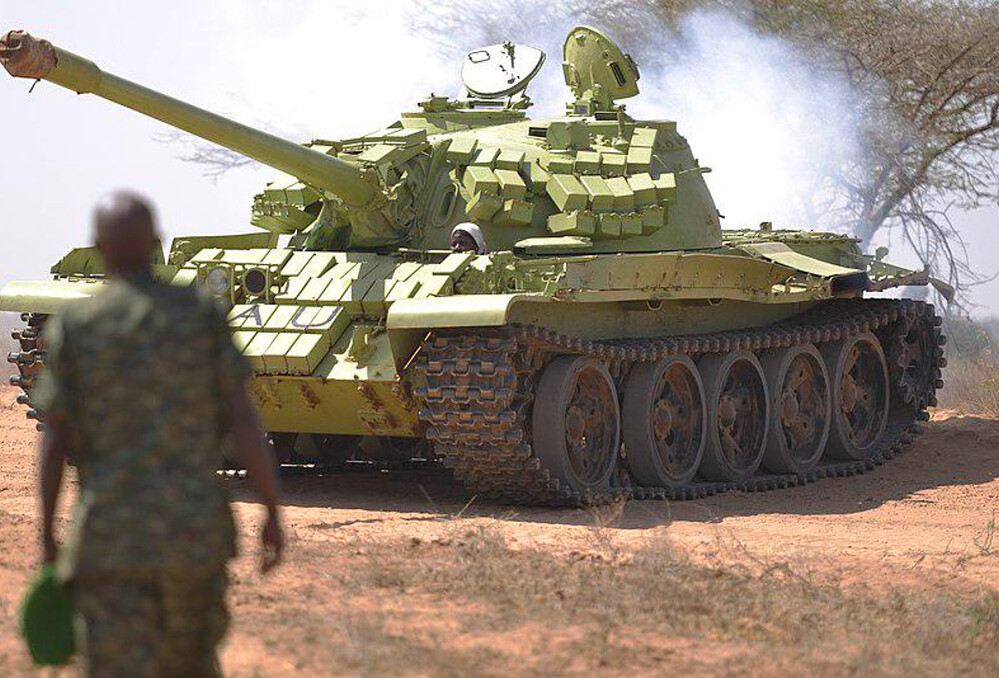
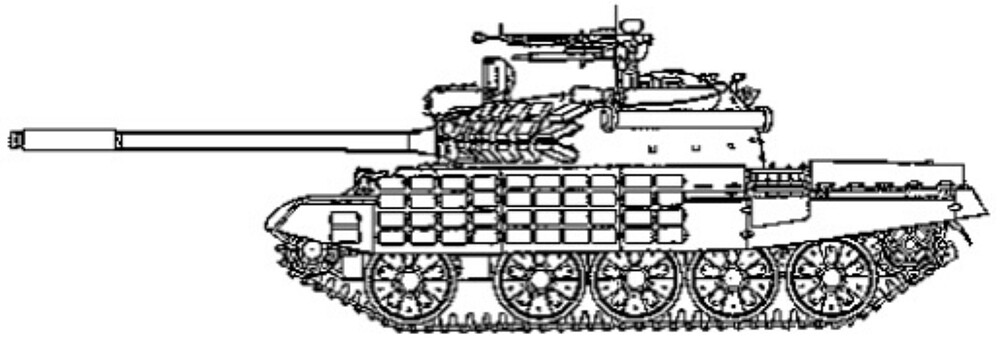
The T-55AMV’s protection is centered around the integration of Kontakt-1 explosive reactive armor (ERA). Unlike the T-55AM, which featured large applique composite armor blocks on the turret cheeks and hull front, the AMV omits this feature entirely, opting instead for a lighter and, more importantly, cheaper ERA layout. The turret front and upper glacis are covered with Kontakt-1 tiles arranged in a dense pattern, offering significantly improved survivability against shaped-charge munitions such as RPGs and ATGMs. These ERA blocks are estimated to increase protection against HEAT warheads by an additional 400–500 mm of RHA equivalent over the base armor. While Kontakt-1 ERA is primarily effective against chemical energy threats, it has negligible impact on kinetic penetrators.
Additional protection includes ERA covered rubber side skirts covering the lower hull flanks, and a full NBC (nuclear, biological, chemical) protection system for crew survivability in contaminated environments. The tank is also equipped with the 902B “Tucha” smoke grenade launchers, mounted on the right side of the turret, offering rapid screening against visual and infrared targeting. Though less commonly mentioned, some later AMV units may also have included internal spall liners, but this remains unconfirmed in open sources.
Armament and Fire Control System
Spoiler
The main gun remains the 100 mm D-10T2S rifled cannon, now enhanced to fire 9M117 “Bastion” gun-launched anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs). These laser-guided projectiles significantly extend the tank’s engagement range and was able to penetrate modern Western armor. The primary gun is complemented by a 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun and a 12.7 mm DShKM heavy machine gun mounted on the turret roof for anti-air and infantry defense.
The fire control system was significantly modernized under the AM/V package. The tank uses a laser rangefinder (KTD-2), a ballistic computer, and the Tsiklon-M1 two-axis gun stabilizer, allowing for more accurate firing while on the move. The gunner’s optics include both day and infrared night channels, giving the tank limited but valuable night-fighting capabilities. The commander’s role remains traditional, with no independent fire control, but overall accuracy and target engagement speed are significantly improved over the base T-55.
Mobility and Engine
Spoiler
To support the increased weight from additional armor and systems the T-55AMV is equipped with an upgraded diesel engine (estimated combat weight of T-55AMV is ~37 tons, compared to T-55AM’s ~40 tons). Depending on the version, it uses either a 620 hp V-55U or a 691 hp V-46-5M engine. This results in a power-to-weight ratio of approximately 18.6 horsepower per ton (V-46-5M). While the top speed remained limited to around 50 km/h, likely due to transmission and drivetrain constraints, the upgraded engine significantly enhanced acceleration and overall responsiveness, especially in off-road conditions. The torsion bar suspension was retained, but reliability was enhanced through the replacement of older components with newer systems adapted from later tanks.
Operational Use
Spoiler
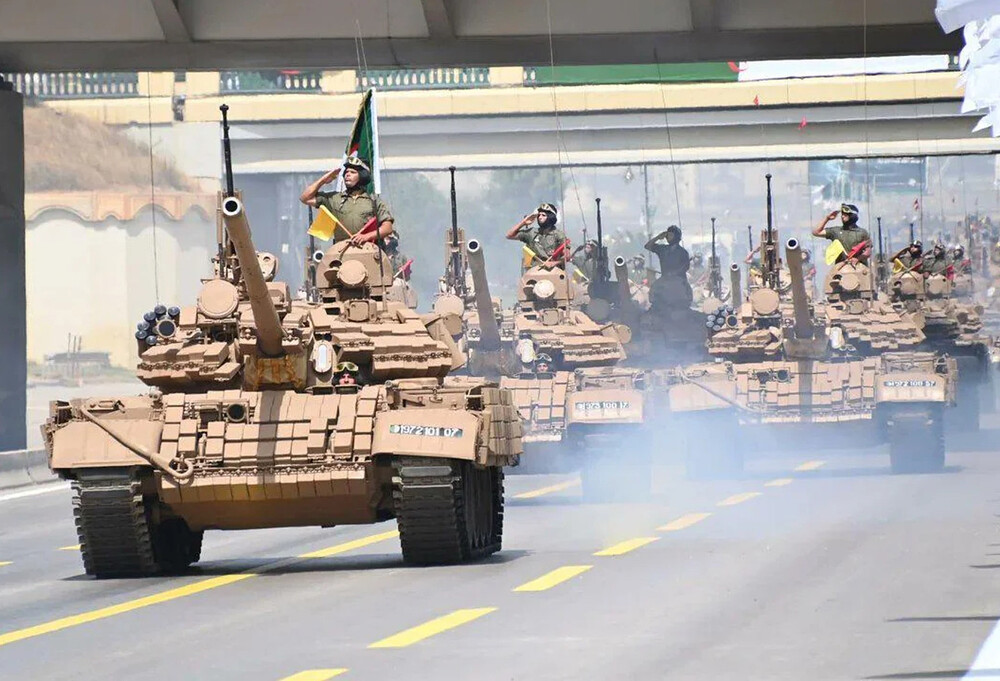
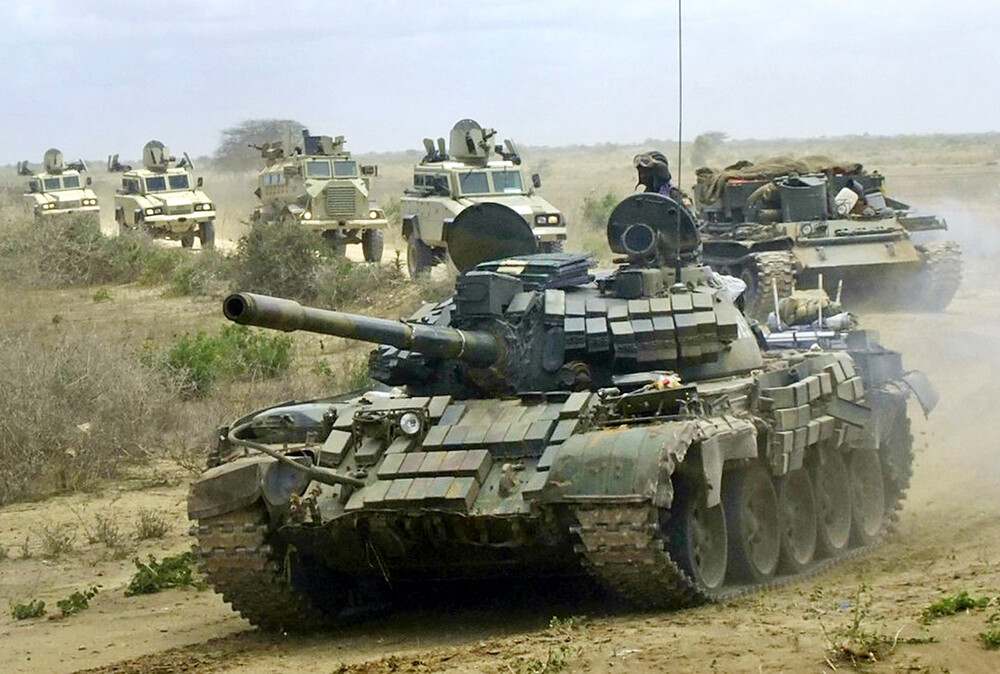
The T-55AMV saw only modest use within the Soviet military itself, primarily as a cheap modernization for reserve units. However, its real success came on the export market. Nations such as Algeria, Syria, and Yemen adopted upgraded T-55s to enhance their armored capabilities at a fraction of the cost of purchasing new main battle tanks. The T-55AMV struck an ideal balance between performance and affordability. Algeria, in particular, became one of the most prominent operators of the AMV variant, reportedly fielding several hundred units. The appeal lay not only in the tank’s enhanced survivability and versatility but also in the logistical simplicity of maintaining an established T-55 infrastructure. Training, spare parts, and tools were all already in place.
In a global market increasingly dominated by expensive MBTs, the T-55AMV represented a cost-effective modernization path for nations that required capable armor without the high investment. Most of the nations that procured these tanks were not preparing to face advanced NATO-style armor but rather engaged in asymmetric conflicts against poorly armed militias or insurgent forces. These opponents typically rely on older RPG-7 variants and early-generation anti-tank guided missiles, precisely the type of threats Kontakt-1 ERA was designed to counter. This made the T-55AMV an ideal choice for regional conflicts where survivability against HEAT-based threats was paramount and where high-tech, expensive armor would be logistically or economically unsustainable.
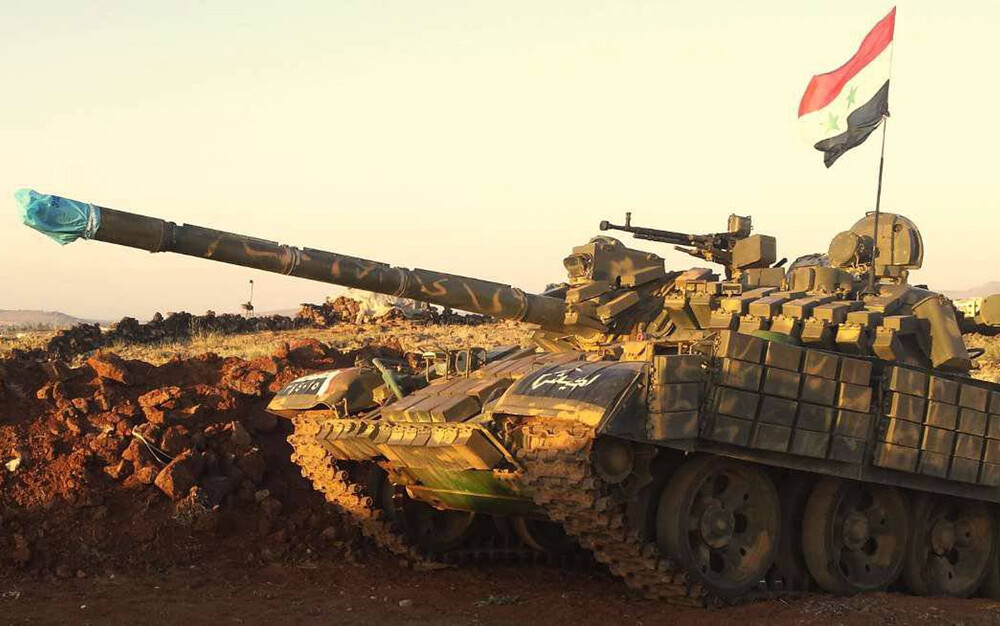
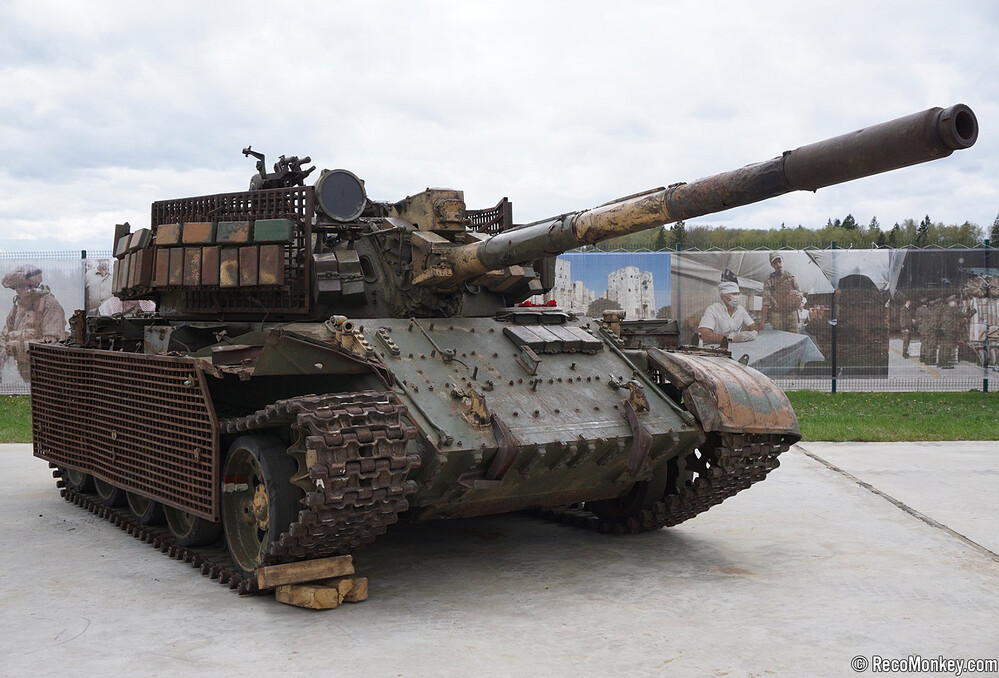
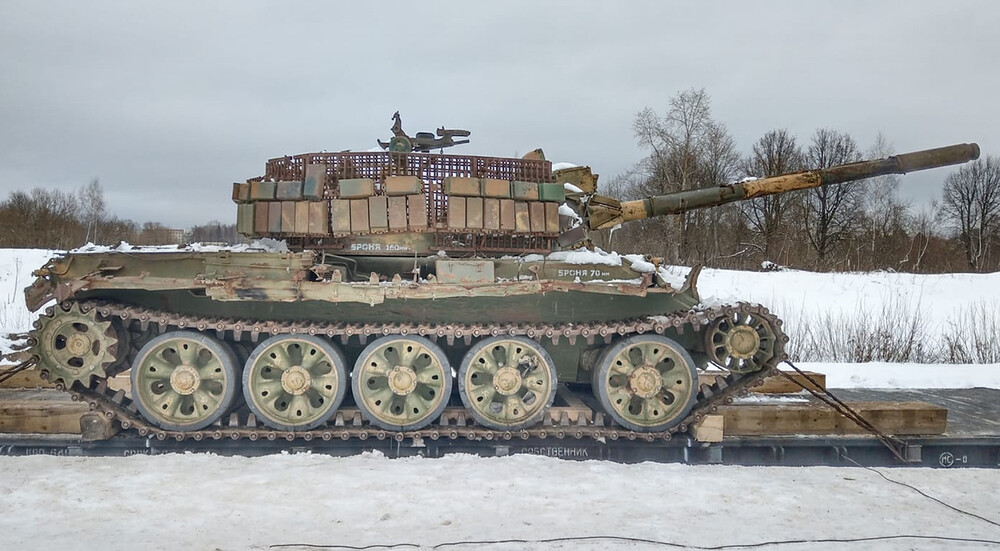
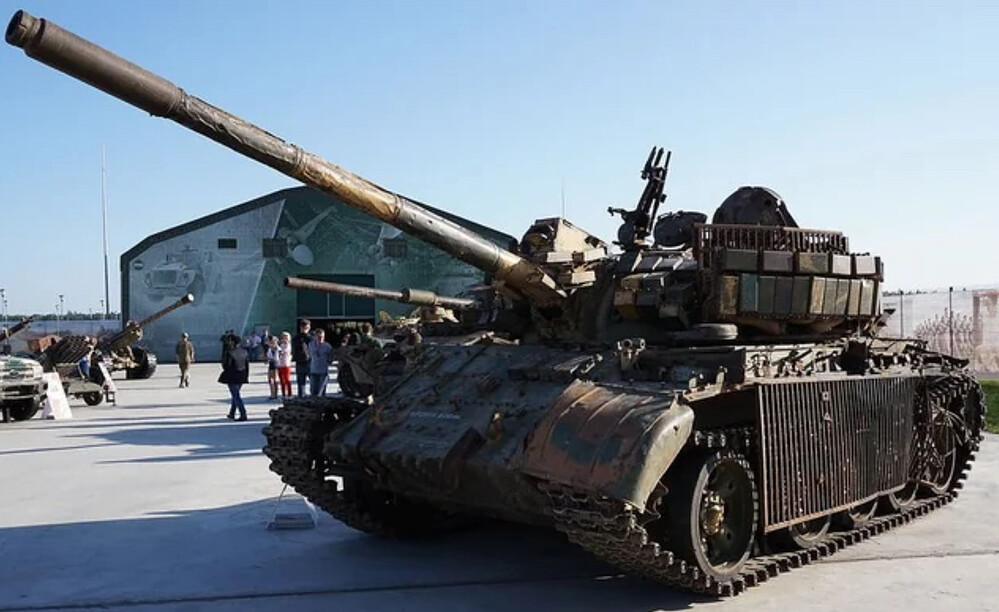
T-55AMV Obr. Zombie
View
This particular example was captured in Syria, and it’s hard to imagine any other tank in the world that can endure such punishment. Few vehicles exemplify battlefield ruggedness quite like the T-55.
T-55AMV Specifications
Spoiler
General Characteristics
- Type: Modernized Medium Tank
- Origin: Soviet Union
- Crew: 4 (Commander, Gunner, Loader, Driver)
- Combat Weight: ~37 tons (with ERA)
- Length (gun forward): 9.0 m
- Width: 3.37 m
- Height: 2.35 m
Armament
- Main Gun: 100 mm D-10T2S rifled cannon
- Stabilized in two planes (Tsiklon-M1 stabilizer)
- Capable of firing standard 100 mm ammunition and
9M117 “Bastion” gun-launched ATGMs - Typical ammo types: APFSDS, HEAT-FS, HE-FRAG, ATGM
- Ammo Load: ~43 rounds
- Coaxial MG: 7.62 mm PKT machine gun (approx. 3,500 rounds)
- Roof-mounted MG: 12.7 mm DShKM heavy machine gun (for anti-air and light targets)
- Smoke System: 902B “Tucha” smoke grenade launchers (8 tubes, 81 mm)
Fire Control and Optics
- Fire Control System: Volna
- Gunner’s Primary Sight: TShSM-32PV day/night sight
- Laser Rangefinder: KTD-2 (integrated with FCS)
- Ballistic Computer: BV-62
- Night Vision: Infrared-based night channel (no thermal imaging)
- Stabilization: Tsiklon-M1 two-axis stabilizer system
Protection
- Base Armor:
- Hull Front: ~100 mm RHA
- Turret Front: ~200 mm cast steel
- Explosive Reactive Armor:
- Kontakt-1 ERA applied to turret, glacis, hull sides, and sometimes roof
- ERA provides up to ~400–500 mm additional protection against HEAT threats
- Additional Features:
- NBC (Nuclear, Biological, Chemical) protection system
- Internal spall liners (possible in some units)
- Rubber side skirts
Mobility
- Engine Options:
- V-55U diesel engine (620 hp)
- Some variants with V-46-5M (691 hp)
- Transmission: Manual, 5 forward / 1 reverse gear
- Suspension: Torsion bar
- Power-to-Weight Ratio:
- ~16.66 hp/ton (V-55U)
- ~18.6 hp/ton (V-46-5M)
- Top Speed (road): ~50 km/h
- Operational Range:
- 390–450 km (internal fuel)
- Up to 600 km (with external fuel drums)
Other Systems
- Communications: R-173 or R-123 radio set
- Infrared Searchlight: L-4A “Luna” IR spotlight (mounted beside gun)
- Snorkel: Optional equipment for deep fording (~5 m with preparation)
Sources
Spoiler
T-55 series of main battle tanks
T-54/T-55 operators and variants - Wikipedia
Omsktransmash announced its readiness to modernize T-55 tanks of foreign armies
Tested by fire: how and why the T-55 and T-62 were upgraded - ВПК.name
Russia offers upgrade of ageing T-55 and T-62 tanks to foreign custome