Would you like to see T-55M6 in-game?
- Yes as a Tech-Tree Vehicle
- Yes as a Premium Vehicle
- Yes as a Squadron Vehicle
- Yes as an Event Vehicle
- No, I don’t want to see T-55M6 in-game.
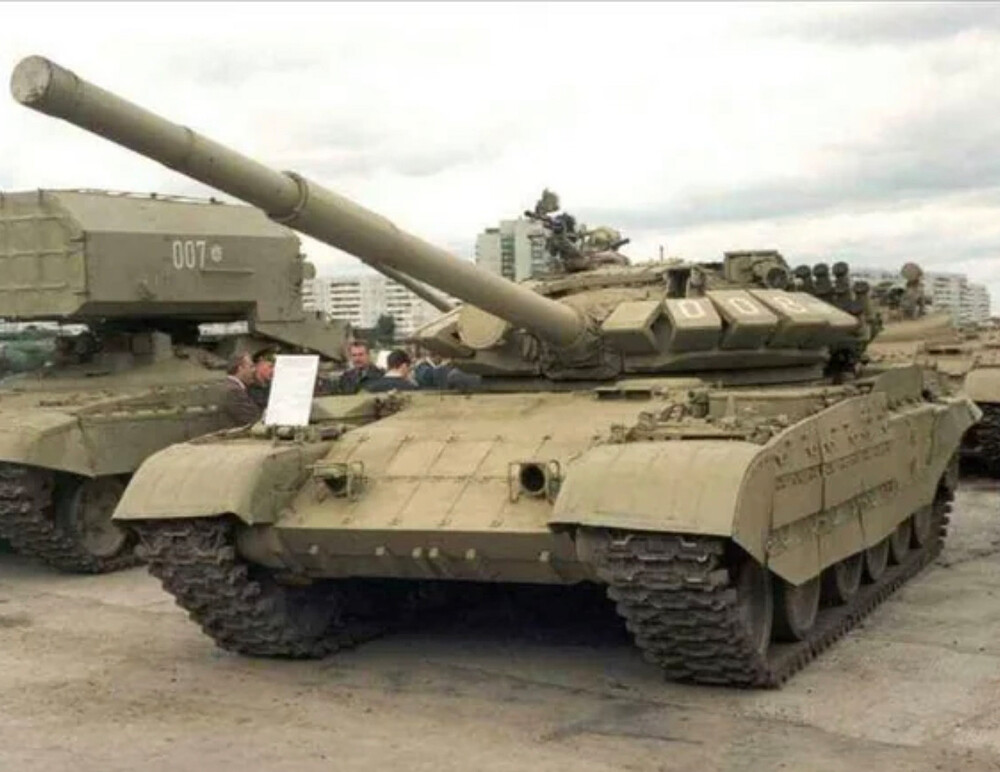
T-55M6 (T-55/72B)
Introduction
The T-55M6 was one of the most ambitious modernization projects proposed for the classic T-55 main battle tank. Developed in post-Soviet Russia, it represented a deep transformation aimed at bringing the T-55’s combat effectiveness closer to modern standards by equipping it with a T-72B (1989) turret. However, despite its advanced features, the modernization ultimately failed to achieve mass adoption due to its high cost relative to the aging platform’s value.
History and Upgrades
Spoiler
The T-55 was developed in the late 1950s as a modernization of the earlier T-54, incorporating improvements based on both battlefield experience and technological advances. It was designed to be reliable, easy to produce, and simple to operate, qualities that helped it become one of the most widely manufactured and exported tanks in history. The T-55 introduced key innovations for its time, such as protection against nuclear, biological, and chemical threats, and automatic fire suppression systems. Armed with a 100 mm rifled gun and protected by all-steel armor, it was considered well-balanced when it entered service. Its adaptability, coupled with low operating costs, made it a favorite not only in the Soviet Union but across dozens of allied and client states. The tank was involved in numerous conflicts for over half a century, from the Middle East to Africa, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe.
However, as armored warfare evolved, the T-55’s combat effectiveness began to diminish. By the 1970s and 1980s, newer Western tanks equipped with more powerful guns and composite armor began to render the T-55 increasingly obsolete on the modern battlefield. In response, multiple upgrade packages were introduced over the years. These included improved fire control systems, laser rangefinders, night vision, reactive armor, and new ammunition types. Variants such as the T-55AM and T-55MV extended the tank’s life by addressing some of its most pressing vulnerabilities, particularly in armor and targeting. Yet even with these upgrades, the core design had clear limits in terms of firepower, and survivability.
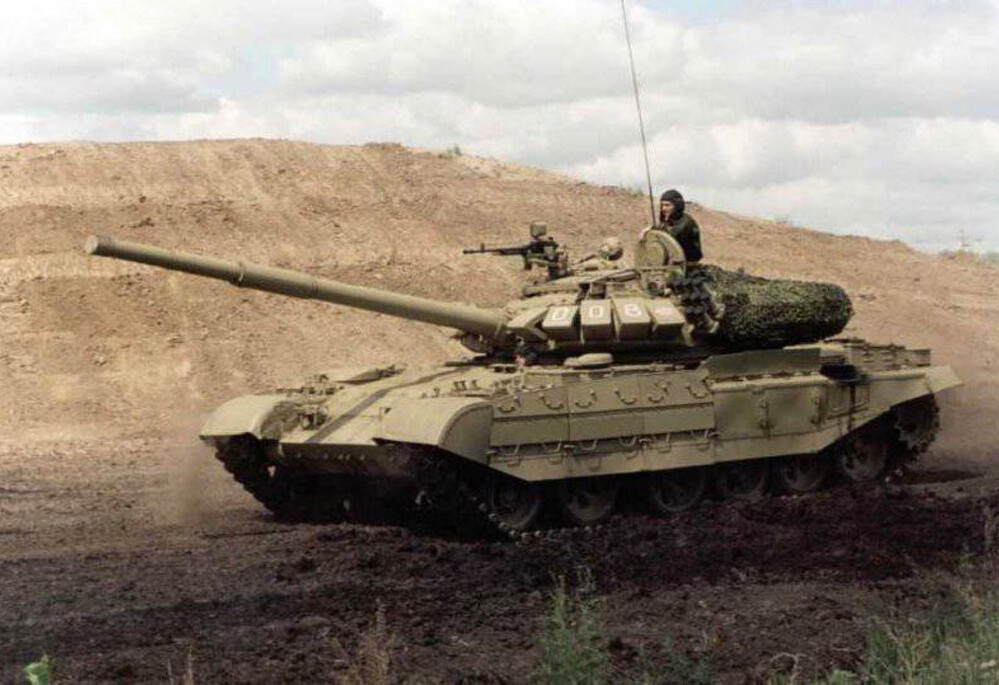
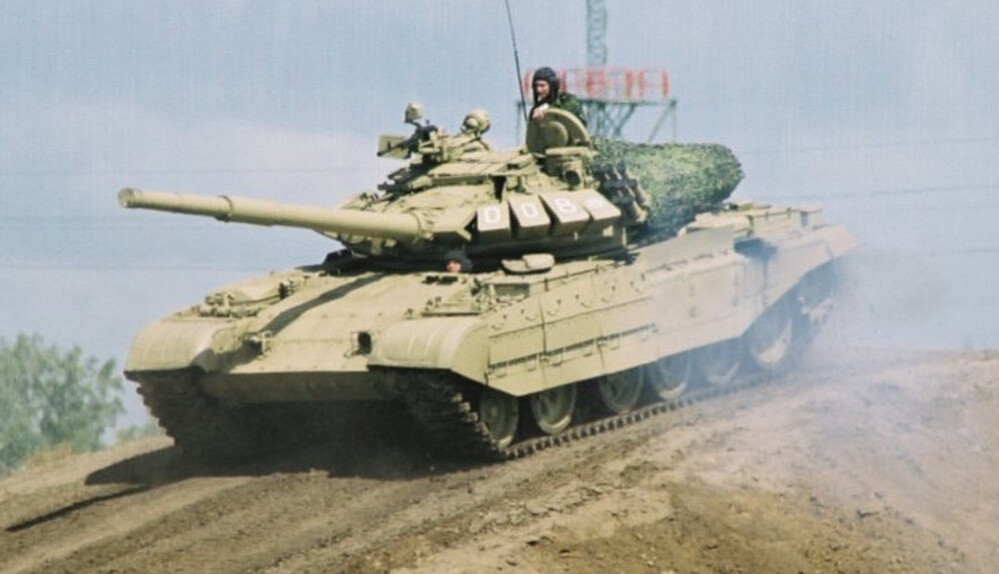
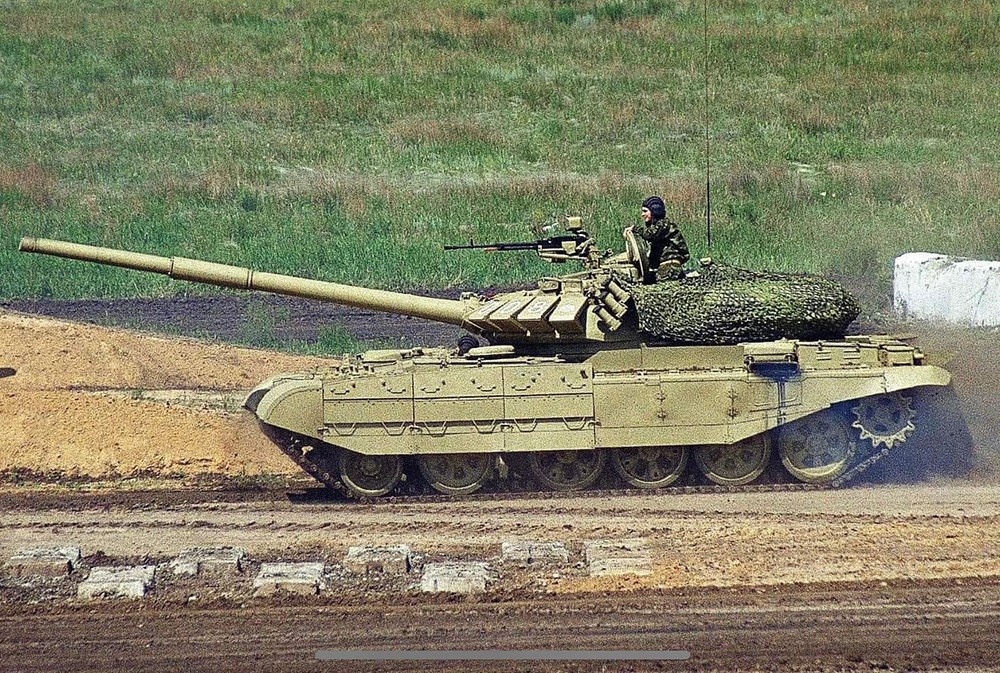
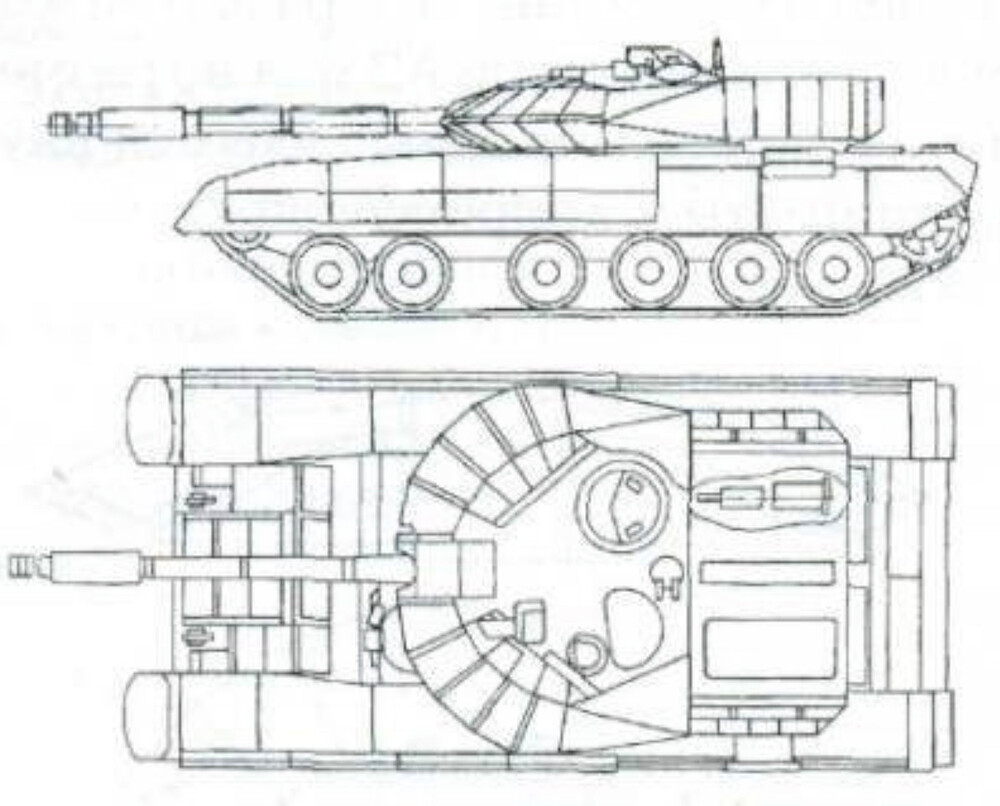
The T-55M6 marked the most ambitious and extensive attempt to bring the aging T-55 platform up to modern main battle tank standards. Unlike previous upgrades that focused on incremental improvements, the M6 represented a fundamental redesign. It featured a heavily modified turret derived from the T-72B (1989), equipped with a 125 mm smoothbore gun, the same main armament used by contemporary Soviet tanks, and fitted with an autoloader mounted at the rear of the turret bustle, allowing for a reduced crew and faster reload times. To accommodate the increased weight and internal changes, the hull was significantly reworked and lengthened, increasing the number of road wheels from five to six. The vehicle was further protected with a comprehensive layer of Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armor across the hull and turret, greatly enhancing its resistance to modern APFSDS and tandem-charge HEAT munitions. However, the fire control system from the T-72B was retained, likely as a cost-saving measure, which may have limited the full modernization potential of the tank’s targeting and engagement capabilities.
Although the T-55M6 offered major improvements in firepower, protection, and survivability, its extremely high upgrade costs relative to the value of the aging T-55 platform prevented it from entering mass production. Potential customers, particularly export markets, found the modernization too expensive compared to purchasing surplus T-72s or newer tanks altogether. As a result, the T-55M6 remained a prototype and demonstration project, highlighting the technical possibilities of deep tank modernization but not achieving real-world success.
Hull Modifications
Spoiler
The T-55M6 retained the original T-55 hull as its base but introduced major external changes. A large extension was added to the front hull, serving multiple purposes: it provided the mounting point for an additional sixth roadwheel per side, supported new composite armor layers, and allowed for the installation of
Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armor on top of the composites. Based on available schematics, the
frontal hull armor of the T-55M6 appears to be largely identical to that of the
T-55AM when stripped of its reactive elements. However, with the addition of
Kontakt-5 ERA, the T-55M6 achieves the highest hull protection of any T-55 variant, surpassing even the
T-55M5 in terms of frontal resistance. That said, despite this significant improvement, its overall hull protection likely still falls short of that found on the
T-72B (1989), which benefits from a more advanced armor layout in addition to Kontakt-5.
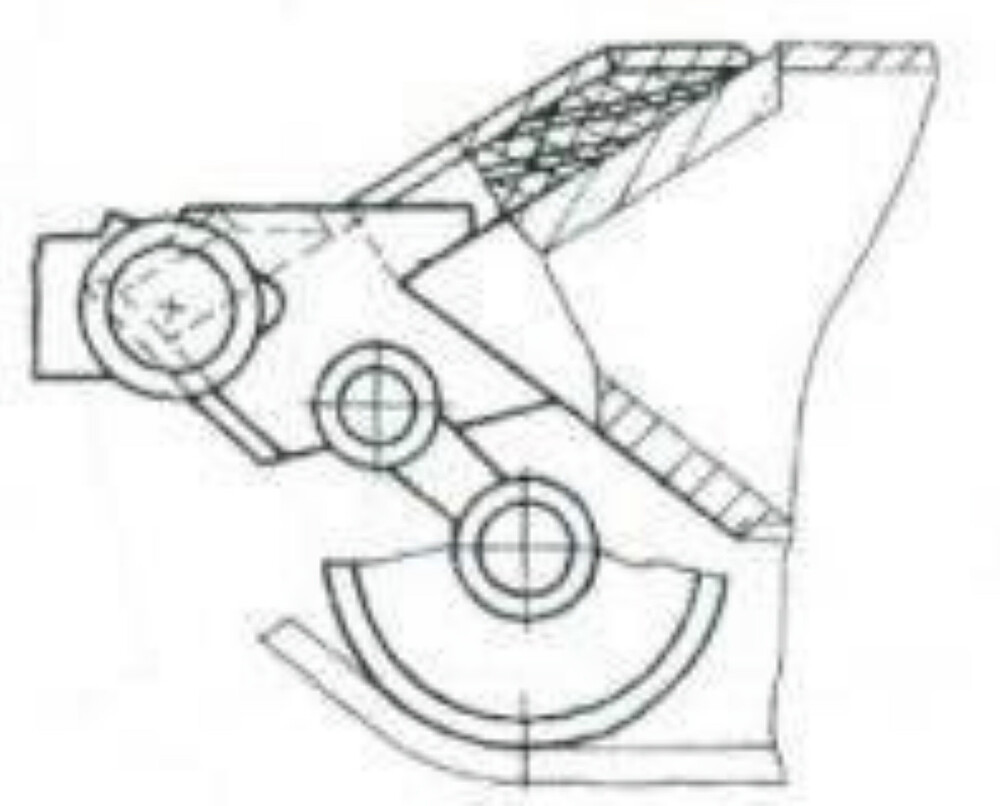
While the underlying original hull structure remained fundamentally the same, these modifications gave the T-55M6 an elongated appearance. The tank’s new suspension arrangement featured six roadwheels per side. The frontmost wheel was a T-80-style wheel, while the remaining wheels were either T-72-style wheels or the original T-55 wheels. The flexible rubber side skirts were retained but reinforced with Kontakt-5 ERA modules, arranged in a manner similar to the side protection layout seen on the T-80U, providing additional defense against shaped charges and light kinetic threats.
Turret and Autoloader
Spoiler
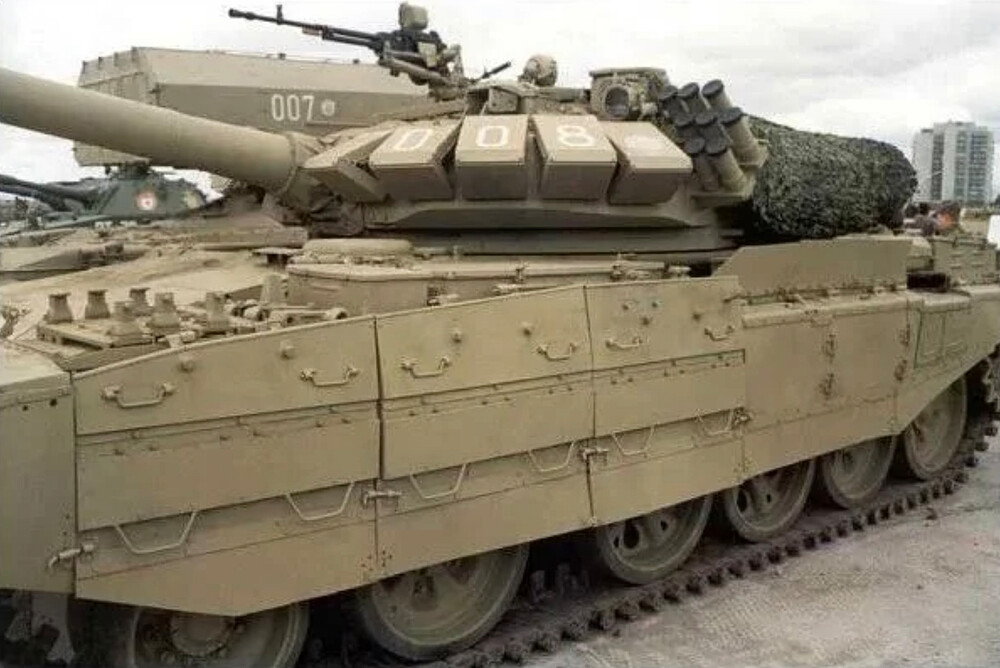
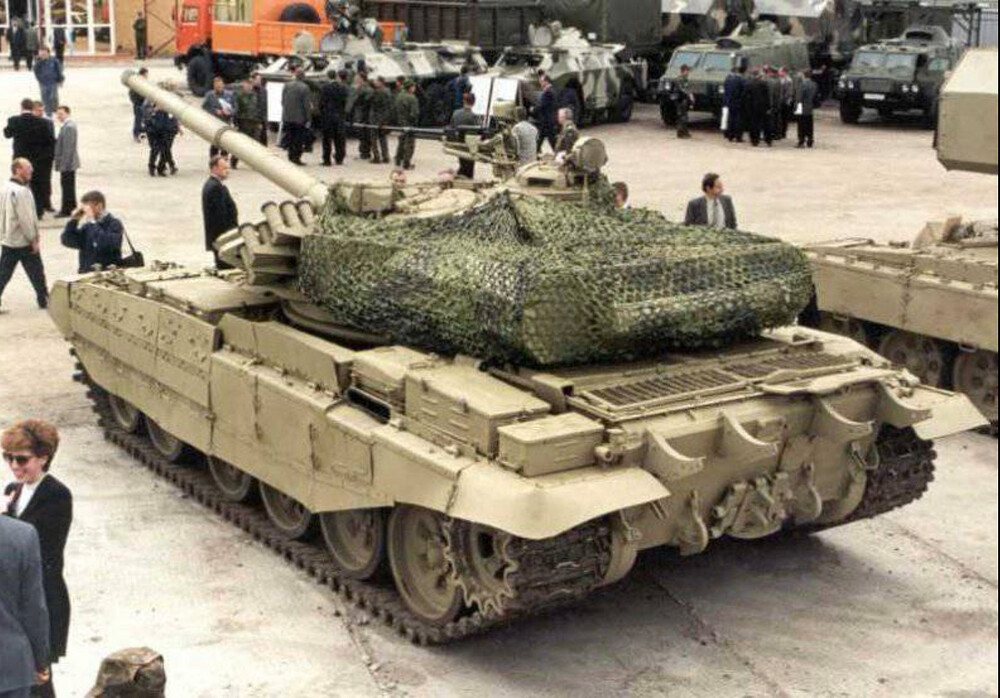
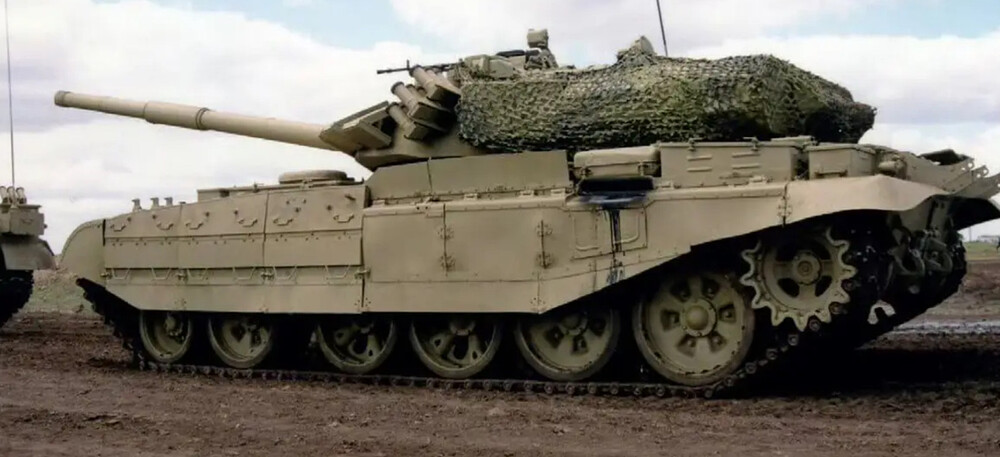
The most significant upgrade on the T-55M6 was its turret, sourced from the T-72B (model 1989) series. The turret offered robust composite armor protection, designed to defeat both kinetic penetrators and shaped charge munitions.
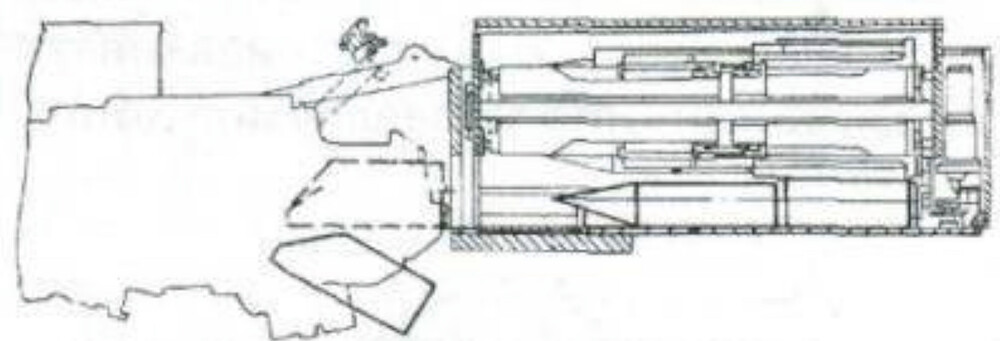
However, unlike the standard T-72B, the T-55M6 turret was modified. The traditional carousel autoloader beneath the turret was supposedly removed. Instead, engineers installed a new armored autoloader compartment located at the rear of the turret, isolated from the crew fighting compartment. This design approach resembled the French Leclerc tank layout and increased crew survivability by physically separating ammunition from the crew. The autoloader was capable of holding 22 rounds of 125 mm ammunition. It remains unclear how much, if any, additional ammunition was stored inside the hull or whether remnants of the original carousel remained in use. Regardless, if there was no carousel, this system allowed the T-55M6 to benefit from autoloaded 125 mm firepower while reducing the risk of catastrophic internal explosions if the turret was penetrated. It is also likely that the T-55M6 was fitted with internal spall liners, similar to those found in the T-55M5, providing an additional layer of crew protection by reducing fragmentation from armor penetrations.
Fire Control and Armament
Spoiler
The fire control system of the
T-55M6 marked a substantial improvement over earlier T-55 variants. While it did not feature thermal imaging, it was equipped with
basic day optics, a
laser rangefinder, and a
ballistic computer, bringing its target acquisition and engagement capabilities in line with early 1990s Soviet main battle tanks. In fact, this fire control suite appears to be identical to that of the
T-72B, offering similar gunnery performance and accuracy under daylight conditions. However, unlike the
T-55M5, which was fitted with a
thermal imaging sight for the gunner, the T-55M6 relied solely on basic IR night vision. This omission likely reflected an effort to control costs and simplify integration, but it came at the expense of reduced night and poor-weather performance. Even so, the T-55M6’s fire control system represented a major leap over legacy T-55 systems, making it far more competitive in terms of long-range and precision engagement.
The main armament was the 125 mm 2A46M smoothbore gun, capable of firing a full range of Soviet munitions, including modern APFSDS rounds, HEAT shells, HE-Frag shells, and 9M119 Refleks (AT-11 Sniper) anti-tank guided missiles. In 2001, the most capable anti-tank round commonly used by the T-72B was the 3BM42 “Mango” APFSDS. This round featured a dual-core tungsten penetrator and could defeat roughly 520 mm of RHA at 2,000 meters under optimal conditions. Although more advanced rounds like the 3BM46 “Svinets” existed, their increased length made them incompatible with the T-72B’s standard autoloader unless modified, making 3BM42 the most effective widely fielded option at the time. Secondary armament included a 7.62 mm PKT coaxial machine gun and a 12.7 mm NSVT heavy machine gun mounted on the now commander’s hatch for anti-aircraft and anti-personnel roles.
Engine and Mobility
Spoiler
The total weight of the vehicle increased by about eight tons compared to a standard T-55. Despite the tank’s significant weight increase, mobility was preserved by installing a V-46-5M diesel engine, producing 695 horsepower. This engine provided a power-to-weight ratio of about 15–16 hp per ton, close to that of the original T-55. As a result, key performance metrics such as maximum speed (~50 km/h on road) and operational range (~500 kilometers) remained largely unchanged from the older T-55 models, ensuring that the T-55M6 could maneuver and redeploy effectively even under the heavier load. The modified chassis, with six roadwheels and reinforced suspension elements, offered improved weight distribution and better cross-country capability, though the tank remained lighter and more compact than larger main battle tanks like the T-80 or T-90.
Implementation
Spoiler
In War Thunder, the T-55M6 would stand out as a remarkable evolution of the T-55 lineage, a hybrid between Cold War-era medium tanks and modern main battle tank technology. It offers a unique combination of legacy design and contemporary upgrades, bridging the gap between older Soviet tanks and more advanced platforms like the T-72B. The most striking feature is its powerful 125 mm smoothbore gun, paired with a rear-mounted autoloader, a configuration not commonly seen on Soviet tanks of its generation. This system not only reduces crew size but also significantly enhances crew survivability. With no ammunition stored in the fighting compartment and the autoloader isolated at the rear of the turret, the T-55M6 could be considered one of the safest Soviet/Russian tank designs ever produced prior to the T-14 Armata, provided additional rounds are not stored in the hull.
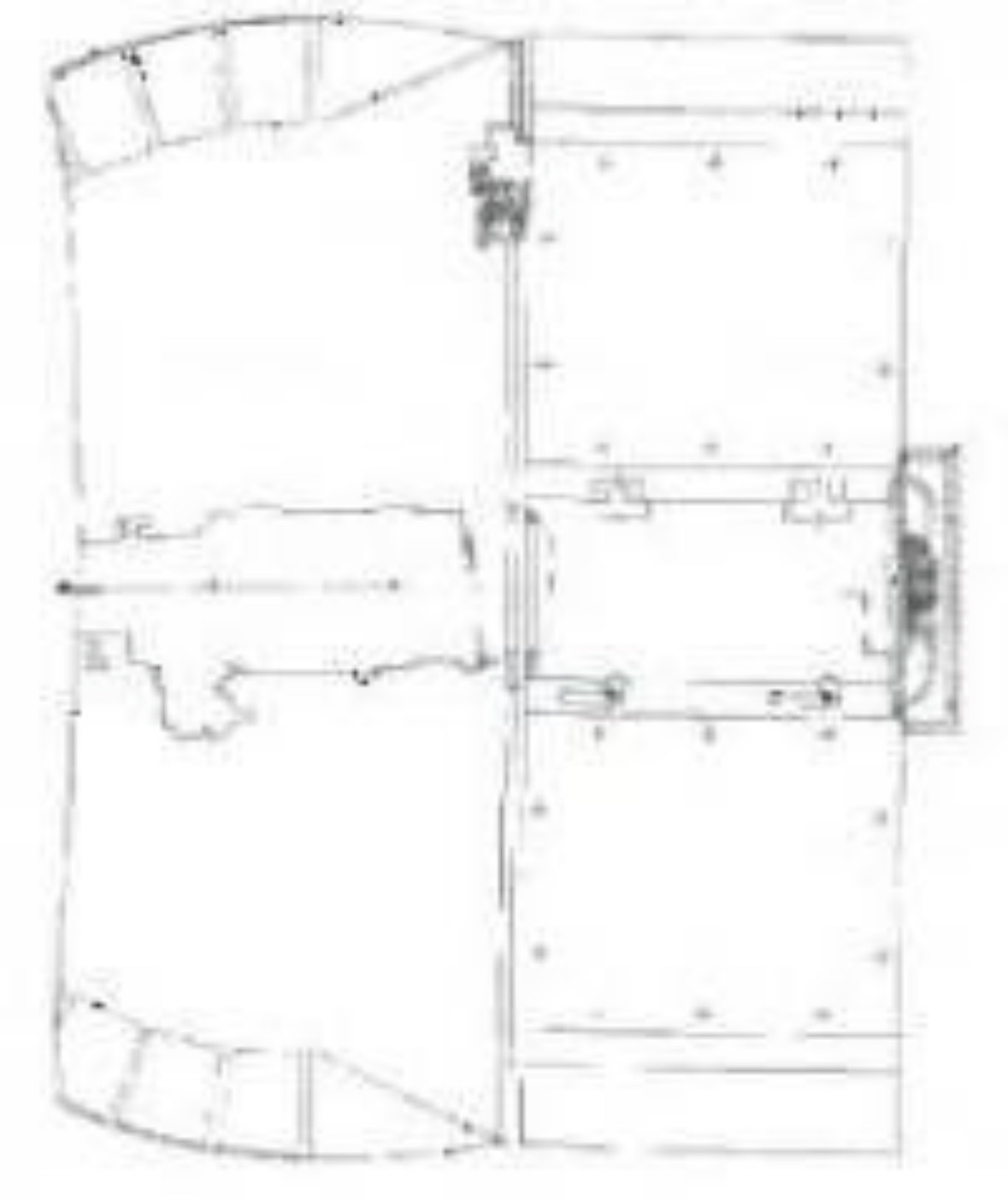
However, a major obstacle to fully implementing the T-55M6 is the lack of detailed technical documentation. Accurate schematics and clear photographs of the tank’s redesigned autoloader system are extremely limited. In most available images, the turret rear is obscured by camouflage nets, making it difficult to assess the exact shape and configuration of the autoloader compartment. Additionally, there is no confirmed data regarding the total ammunition load carried by the tank or how ammunition was distributed internally beyond the 22 rounds loaded into the rear autoloader. Without this information, recreating the tank with complete accuracy remains a significant challenge.
Specifications
Spoiler
- Primary Armament:
- 125 mm 2A46M smoothbore gun (autoloader, 22 rounds in isolated armored compartment)
- Secondary Armament:
- 7.62 mm PKT coaxial machine gun
- 12.7 mm NSVT heavy machine gun (roof-mounted)
- Fire Control and Optics:
- Basic night vision
- Laser rangefinder
- Ballistic computer
- Turret:
- Protection:
- Composite armor glacis with extension
- Kontakt-5 ERA on turret front, hull glacis, and hull sides
- Rubber side skirts
- Smoke launchers
- Engine:
- V-46-5M diesel engine, 695 horsepower
- Mobility:
- Top speed: ~50 km/h
- Power-to-weight ratio: ~15–16 hp/ton
- Lengthened hull with six road wheels (T-80 front wheel, T-55/72 style rear wheels)
- Crew:
- 3 (Commander, Gunner, Driver)
Existing Schematics
Spoiler
Sources
Spoiler
https://en.topwar.ru/25222-osnovnoy-tank-iz-srednego-modernizaciya-t-55.html
Comprehensive Soviet/Russian vehicle collection
T-55 series of main battle tanks
Below The Turret Ring: Explosive Reactive Armor - some history, some types
Tankograd: T-72: Part 1