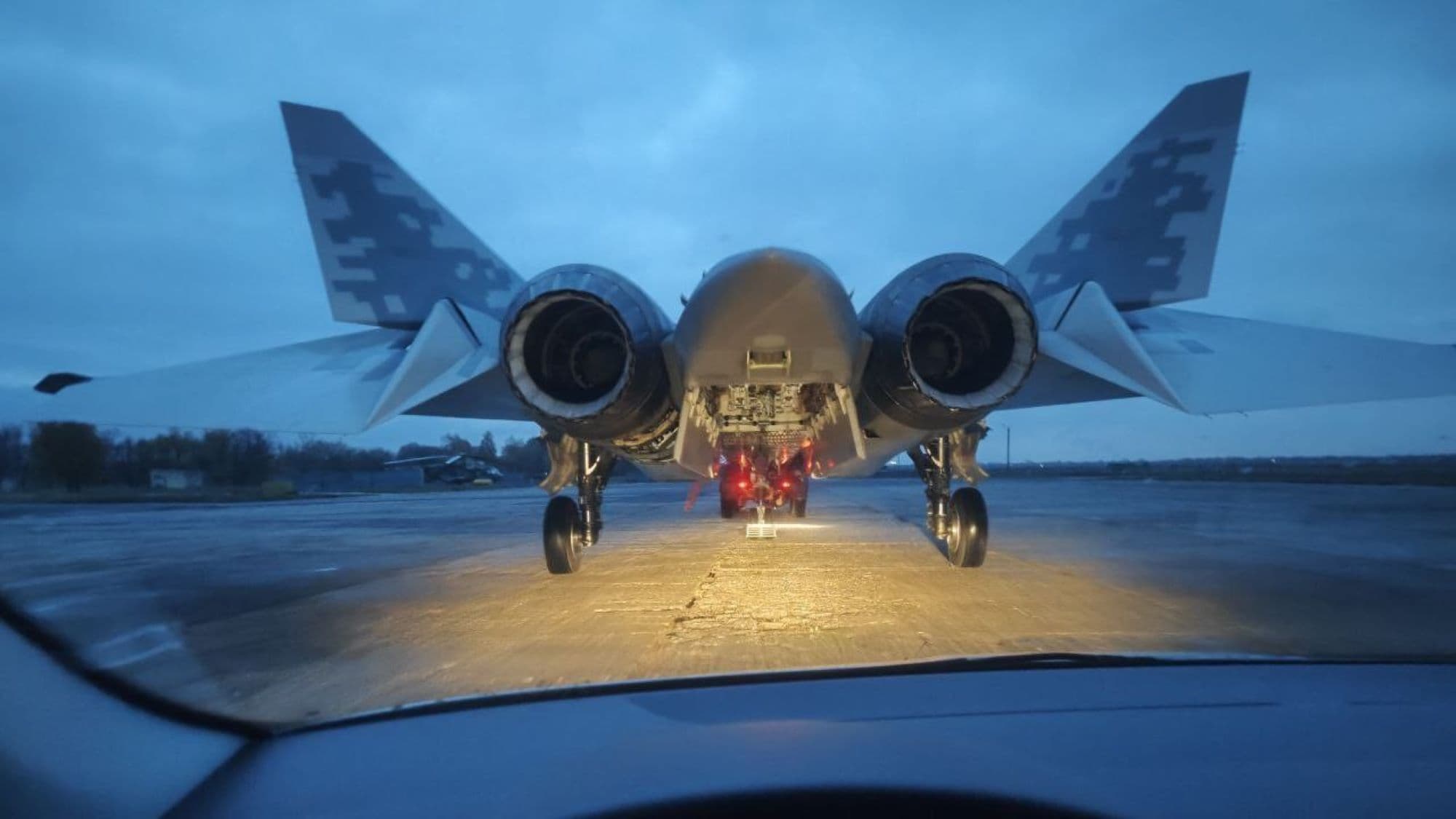
Work In Progress, Feel Free to post any information or discuss about it !
Variants
T-50
Spoiler
WIP
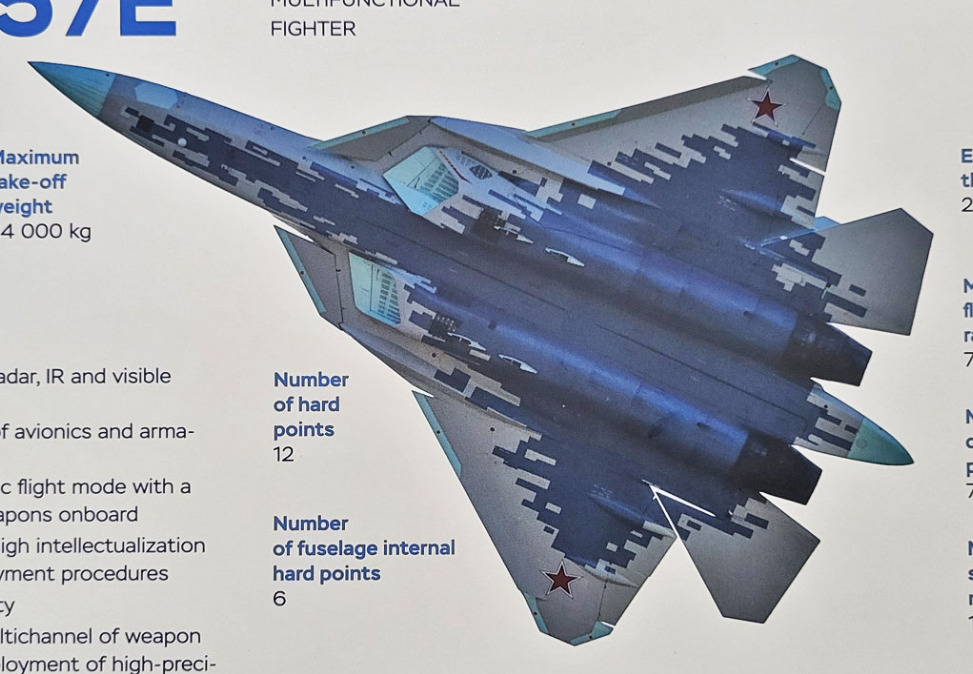
Su-57
Spoiler
The base Su-57 variant, entered service in 2020.
Also known as Phase I Su-57 which incorporates the older Al-41 engines
Electromagnetic Suite
Spoiler
Su-57 Features a Multitude of Arrays, Each performing their unique task and linked together towards each other via Sh-121 system.
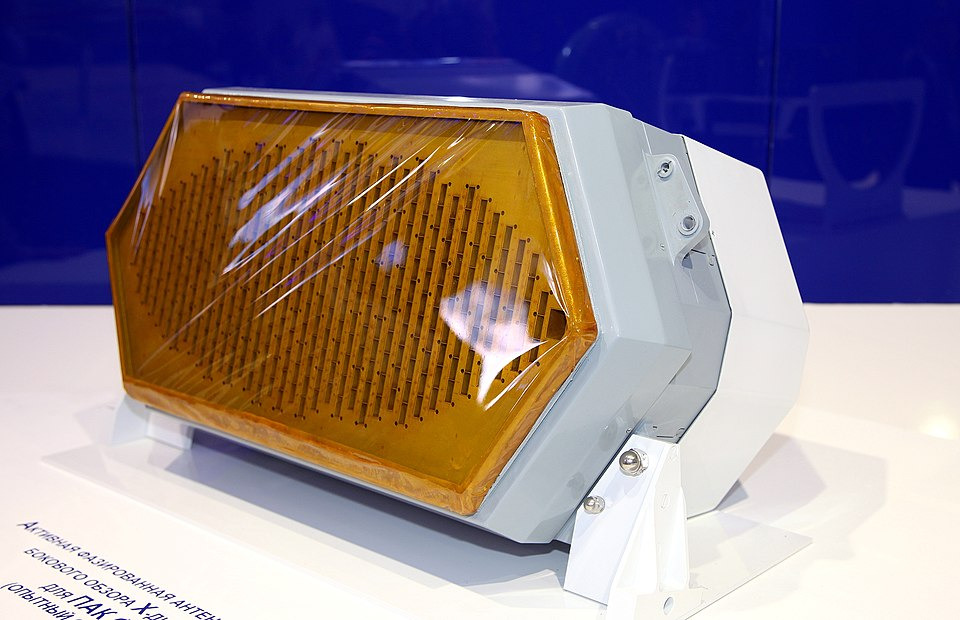
1) N036
Named Byelka or Squirrel, Has 3x X Band systems and 4x L band system
- Main Array
AESA RADAR. Contains 1500+ TRMs (The no. of Modules vary for different prototypes, serial array installed on Aircraft hasn’t been seen) The TRMs are GaAs based.
Both +/- 60 degrees electronic scan gimbal horizontally and vertically. Features SAR mode.

-
N036B
AESA RADAR. Contains 350-450 TRMs, GaAs Based. Both +/- 60 degrees electronic scan gimbal horizontally and vertically. Features SAR mode.

-
N036L
Comprises of 2 different L band linear arrays, SiC based TRMs. The one in the wing slats are used for IFF. Ones in the LEVCONS are Multi Purpose Arrays.
The whole Byelka (N036) Complex can track (TWS) 60 targets at a time and engage 16 altogether (Datalink Channels)
All these Arrays Work together with sensor fusion. All the arrays are meant to work as Multi Purpose array (except wing slats). They perform function of ECM, PD MAWS and RWR (Signal Sniffing)
An Added point for N036L :- These Arrays are 2D and not meant for fire control System. However due to them being L Band, they can detect stealth jet relatively easy, Hence via sensor fusion, they increase the efficiency of scan rate of the X band radars by cueing the X band radars in the general direction of target in narrow beam mode.
2) L402
Named Gimalaya or Himalaya, is a ECM suite of The Su-57, It incorporates all the Arrays of Su-57 Along with :-
-
4x Arrays on Wingtips

-
A X Band array in the rear “stinger”
These Also act as Multipurpose Arrays
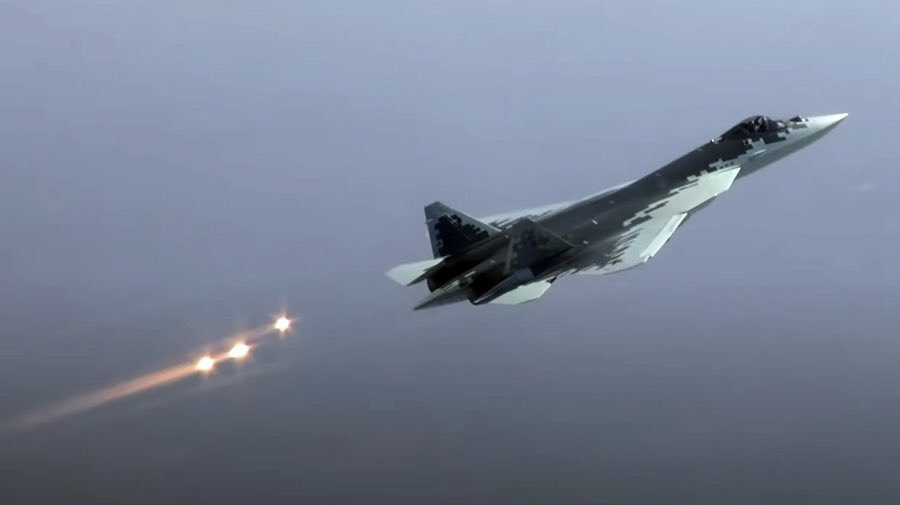
Another Noticeable Addition in this Suite is the UV-50-01 Countermeasure Dispensing System, Su-57 features 3 of these facing downwards and 2 towards side. The main crux for their ECM function is the presence of Expendable ECM transmitter decoys like BriteCloud


(Source :- Su-57 Felon, Piotr Butowski)
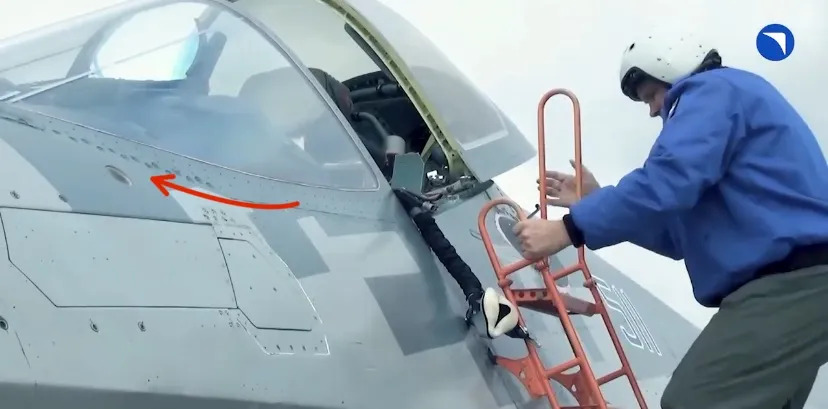
Su-57 also incorporates other small Transmitters like N036Sh , The IFF antennas, seen by the 3 white-grey dots on the nose of the aircraft
Electrooptical Suite
Spoiler
Su-57 Has its own characteristic 101-ks-_ EO suite which makes it very unique :-
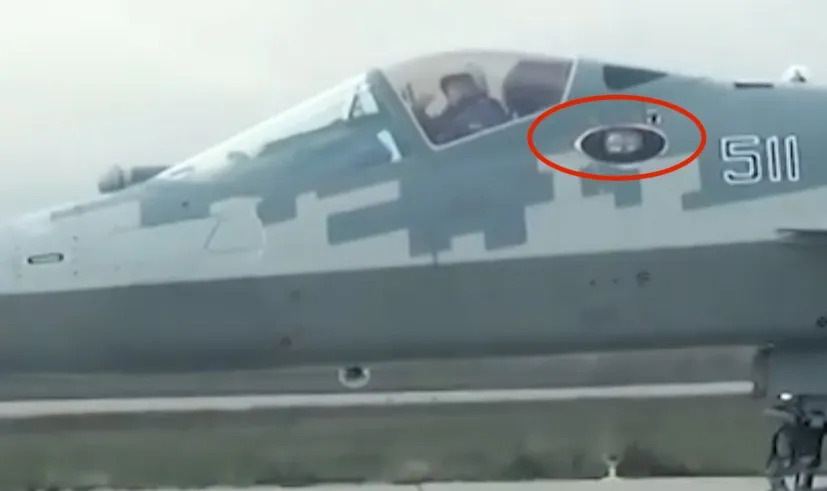
1) 101-KS-V (OLS-50M) :- It is a IRST which IR and TV ability. It can detect Far away targets both frontally and from rear, The most important thing about this system has to be its capability to laze and drop laser weapons via the laser in the IRST, essentially like a targeting pod. When not in use, it turns around, and now from the front, only a thick RAM coated IRST housing is visible
2) 101-KS-U :- It is a set of UV MAWS providing 360 degrees coverage of incoming missiles in the UV spectrum. There are 4 of these sensors, 2 at the sides of the nose just behind the canopy, 1 below the nose and 1 above the rear “sting”.
3) 101-KS-O :- A set of LDIRCM consisting of 2 Turrets. Their Task is to Shine a laser onto incoming missiles seeker to essentially burn them rendering them useless. They also perform like IRST, essentially giving this plane 3 IRST with a 360 degrees coverage.
Here The spinning of the DIRCM scanning the sky is also visible, scan rate being around 3 seconds~
https://media.discordapp.net/attachments/305084948619067397/1399171373355499691/felondircm.gif?ex=691fa3e2&is=691e5262&hm=ec2448689c2dea6e0bdbadf140c547303edc46aafe2027fc5bad943aed9c953c&=&width=400&height=140
4) 101-KS-P :- A IR camera present on the Armpit of the triangular Bays, Helps to assist in Landing in bad weather quality conditions, Apparently the footage of this can also be displayed on the Vison of Su-57 HMD (As of now, seems to be meant for Su-57M, Current Su-57 Also might lack HMS)
5) 101-KS-N :- A Targeting Pod faceted from the front, similar in looks of the Sniper Pod.

Along With this, UV-50-01 Dispensers also come in role here dispensing IR Decoys, Flares.



Cockpit
Spoiler
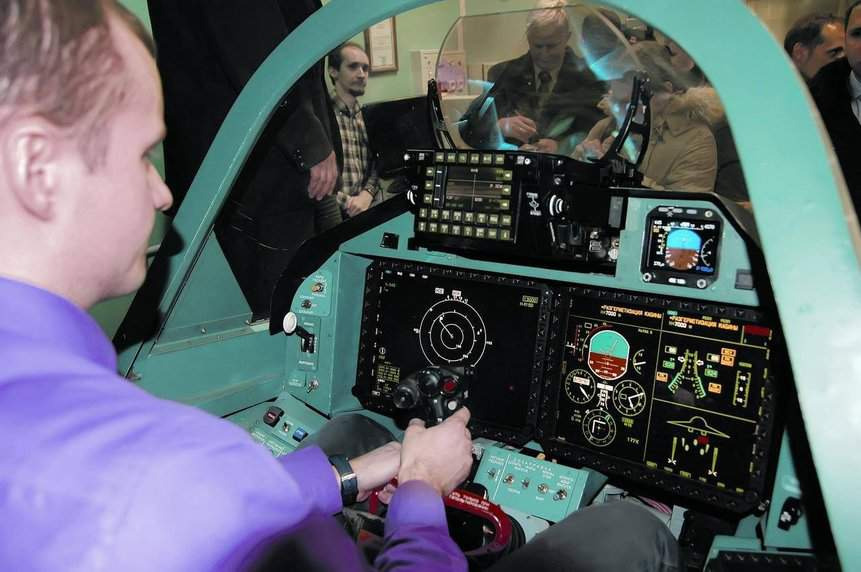

The current Serial Su-57 Features This cockpit, there are changes in Export and Megapolis Felons too.
HUD (The Actual HUD in this is different however, but the display layout is likely the same):-
MFDs :-



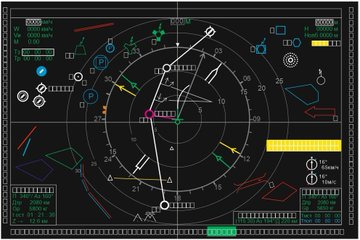
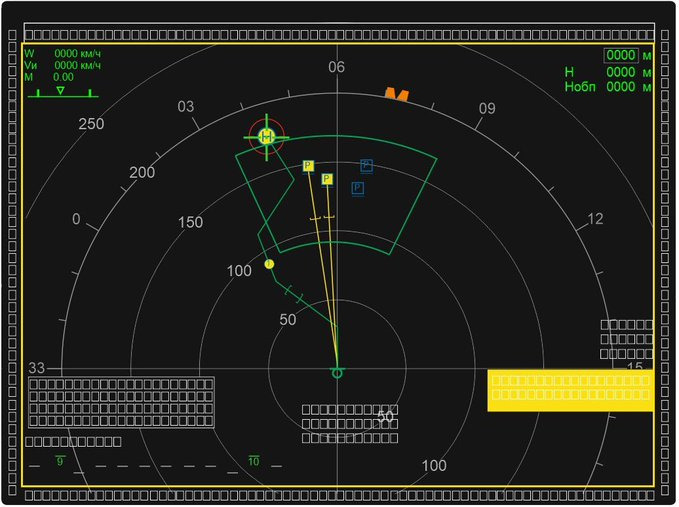
Specifications and Flight performance
Spoiler
NOTE REGARDING MAX SPEED :- Su-57 Is able to go to Mach 2.4 at altitudes, but however is limited to Mach 2 due to RAM limitations

-
Length: 20.1 m (65 ft 11 in)
-
Wingspan: 14.1 m (46 ft 3 in)
-
Height: 4.6 m (15 ft 1 in)
-
Wing area: 78.8 m2 (848 sq ft)
-
Empty weight: 18,500 kg (40,786 lb)
-
Gross weight: 26,700 kg (58,863 lb) normal takeoff weight, 29,770 kg (65,630 lb) at full load
-
Max takeoff weight: 34,000 kg (77,162 lb)
-
Fuel capacity: 9,700 kg (22,700 lb)
-
Powerplant: 2 × Saturn AL-41F1, 88.3 kN (19,900 lbf) thrust each dry, 142.2 kN (32,000 lbf) with afterburner, 147.1 kN (33,100 lbf) in emergency power
-
Maximum speed: Mach 2, 2,135 km/h (1,153 kn; 1,327 mph) at high altitude
- Mach 1.1, 1,350 km/h (729 kn; 839 mph) at sea level
-
Supercruise: Mach 1.3, 1,400 km/h (756 kn; 870 mph)) at high altitude
-
Range: 3,500 km (2,200 mi, 1,900 nmi) subsonic
- 1,500 km (932 mi; 810 nmi) supersonic
-
Combat range: 1,250 km (780 mi, 670 nmi)
-
Ferry range: 4,500 km (2,800 mi, 2,400 nmi) with 2 outboard fuel tanks
-
Service ceiling: 20,000 m (66,000 ft)
-
g limits: +9.0
-
Wing loading: 371 kg/m2 (76 lb/sq ft) normal takeoff weight
-
Thrust/weight 1.09 at normal takeoff weight (0.97 at loaded weight with full fuel)
Fuel capacity calculations
Fuel system. Volume 11.68 m3. Fuel weight 11.68 m3 * 775 kg/m3 = 9000 kg

(Thanks to Paralay for this)
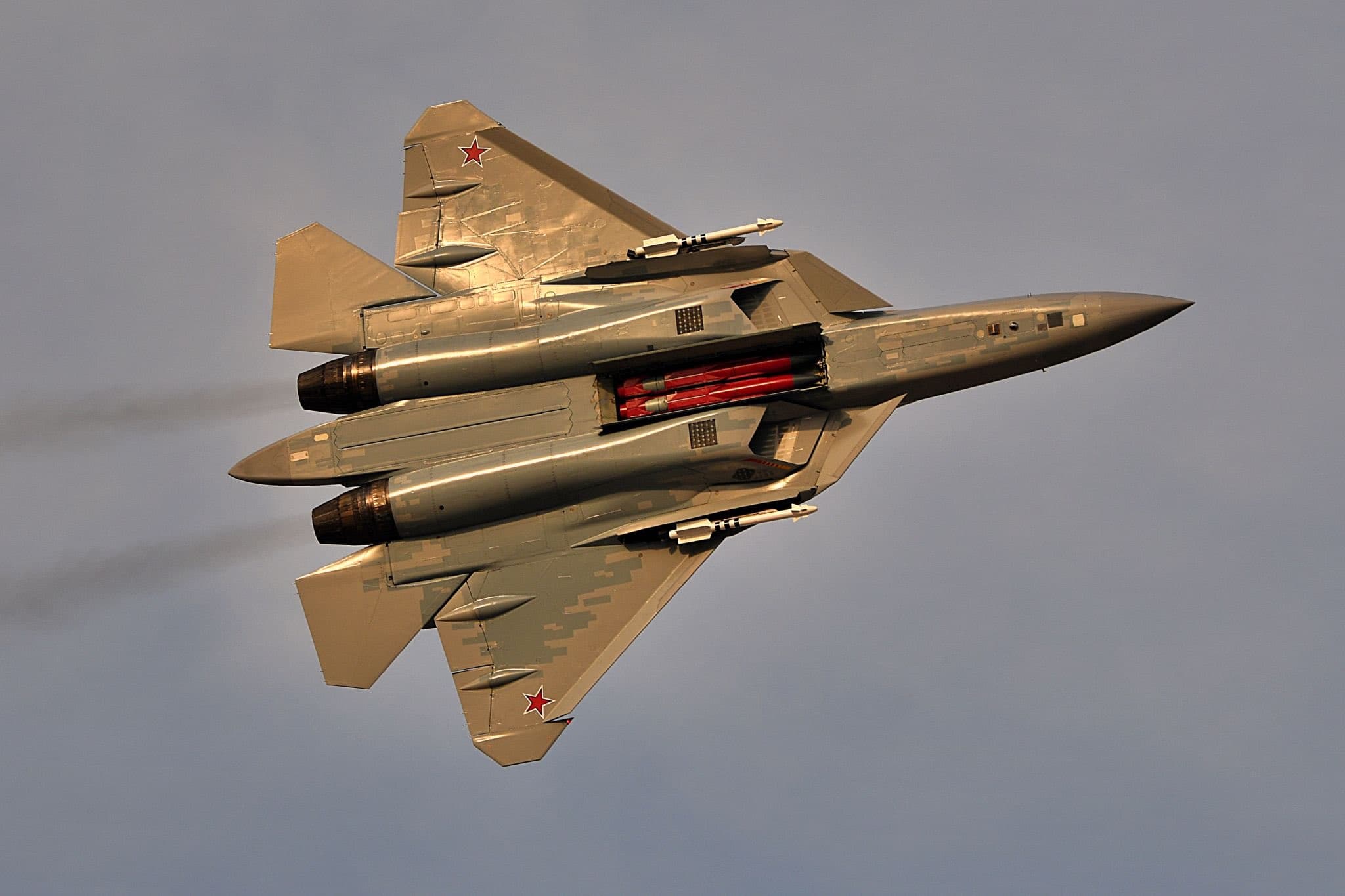
Weapons
Spoiler
Finding the possible weapons of Su-57 is really hard, it doesnt help the fact we dont have a single picture of its main internal weapon bays, hence some assumptions had to be made here.
Gun
- Gsh-30-1 30mm autocannon
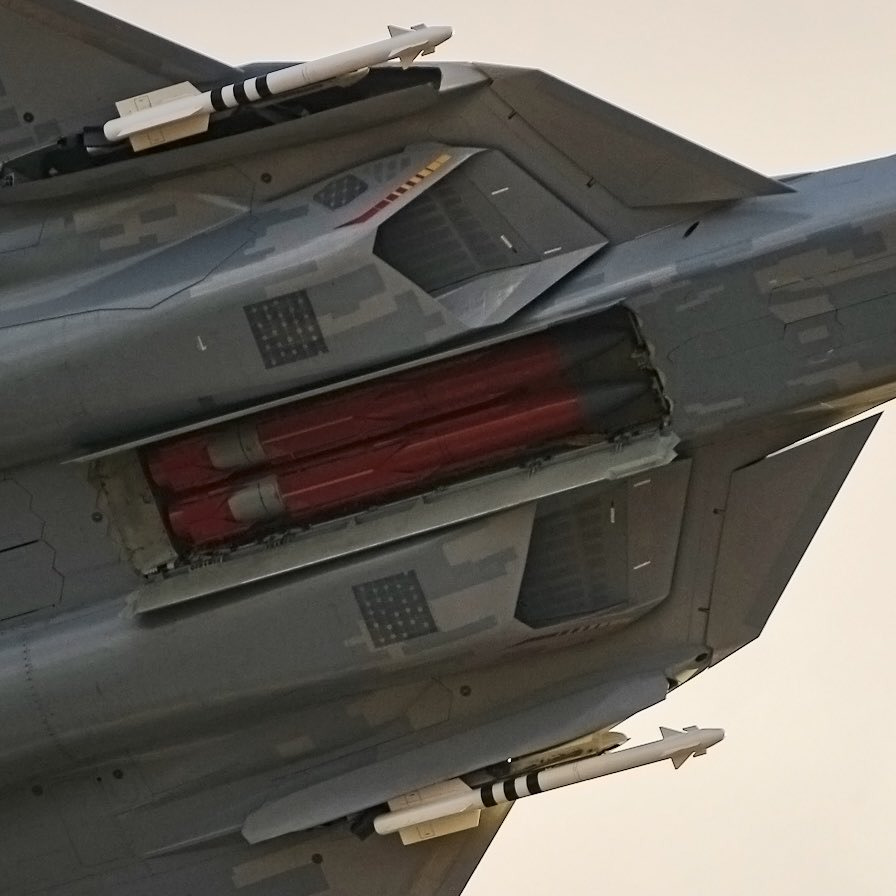
Internal Bays
-
Main Internal Bays
-
4 x R-77M (Izdeliye 180) ( possibly 6 with triple rack according to patent, however not acquired by russian airforce )
-
4 x Izdeliye 810 ?
-
4 x Kh-59MK2/69
-
4 x Kh-58Ushk
-
4 x Grom 1/2
-
4 x Kh-38M
-
4 x Kab-250
-
Weapon bay Fuel tank (Small/Big)
-
-
Side Internal Bays
- 2 X R-74M2
External Pylons
-
Inner wing pylons
- 2x R-77M (Izdeliye 180) (possibly 4) ?
- 2x K-77ME (Izdeliye 180 BD) ?
- 2x Kh-59 (not MK2)
- 2x R-77-1 (possibly 4)
- 2x R-37M / RVV-BD
- 2x Kh-31A/P
- 2x Drop Tanks (2000L/3400L)
-
Outer wing pylons
- 2x R-77M (Izdeliye 180)
- 2x K-77ME (Izdeliye 180 BD) ?
- 2x R-77-1
- 2x R-73/R-73M/R-74/R-74M/R-74M2
Dumb munitions on all external pylons.
- Under Intakes
- 1x 101 KS-N Targeting pod
- 2x R-37M / RVV-BD
- 2x R-77M
- 2x R-77-1
PLEASE NOTE
Su-57 CANT carry R-37M internally, however, according to the export videos, su57e can carry 4 rvv-bd externally.
Izdeliye 810, A special variant of R-37M is being made, incoporating a AESA seeker, smaller central fins, foldable rear fins, and a longer size (hence extended range) for the Su-57.
K-77ME/Izdeliye 810 are still in testing phase, they have not been inducted in service yet.

Interesting Pictures
Stealth Analysis
Spoiler
Finding official stealth capabilites of any 5th gen fighter is impossible without access to sekrit spicy docs.
We will try to find the extents of Su-57 stealth capabilities from the information and simulations we have.
However, we have to bust some rumours to go ahead
-
Exposed screws :-
-
The exposed screws problem was mainly limited to T-50, the old Su-57 prototypes which didnt really need the finishing. Serial Su-57 are much cleaner. Other than that, the radar return from the screw heads for X bands or lower would be negligible, as the screw heads are smaller than the wavelength of the radar waves, hence they dont act as a effective reflecting surface. Some diffraction might occur due to change of material on surface, but they will still be a lot less. Other than that, even planes like F-22 have a lot of exposed screws.
-

-
-
Circular IRST
-
The Circular IRST is often considered as a large source of reflection for Su-57, which isnt wrong, but isnt completely right either. The IRST of the Su-57 Rotates backwards, exposing a surface which is covered with a thick layer of RAM, this smooth surface would actually not cause any diffraction due to sudden change in angle of the surface, which a faceted IRST might do.
-

-
-
Exposed Fan blades
-
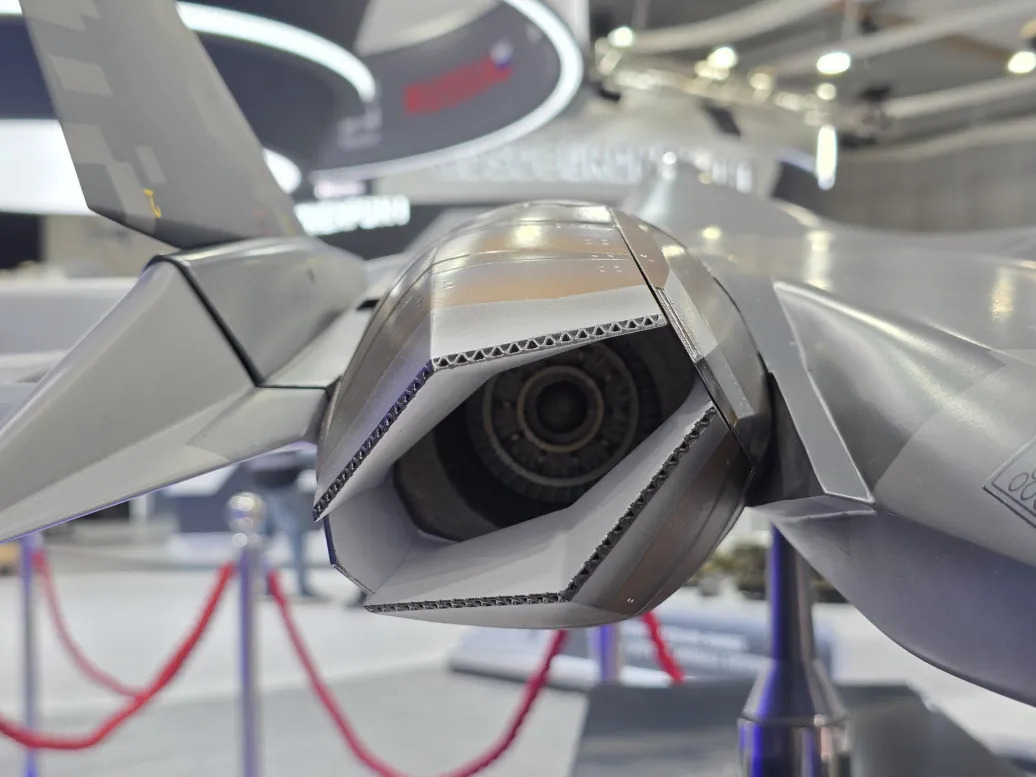
Su-57 uses partial serpentine intakes rather than something on F-22 or F-35. This helps in weight reduction and requires less support structures. However, this causes the fan blades of the engine be exposed from the front. But this is mitigated by using variable ramps, which usually go down post mach 1, and help hide the engine blades from front. Other than this, radar blockers are also implemented angled upwards. The point is to cause multiple reflections through RAM coated intake surfaces to make the radar waves very weak to detect.
-

-
-
RCS comparable to Super hornet
-
People usually say the RCS of su-57 is comparable to a super hornet, which is completely wrong. RCS of super hornet is said to be at 1m2, which is the lowest possible return at only specific angles. It also does NOT consider the fact that the 1m2 value is without any weaponry, which is not what a fighter jet will go against.
-
Other than this, we dont know the real RCS of Su-57. People usually refer to the old T-50 prototype documents RCS ( 1 - 0.1m2 as a goal ) Which did NOT incorporate RAM over external surfaces, other than the IRST and the intakes, nor it considered radar blockers for the intakes.
-
Even if its RCS is 1 - 0.1 m2… in comparison to what is it bad against? people refer to F-22 with 0.0001m2 but forget its again, the lowest possible rcs. Not to mention the fact that it wasnt mentioned that at what frequency is that RCS achieved? There are unclassified CIA documents confirming that hey have been deliberately leaking false values through public media in the past with B-2 ( Credit to Qu_Rahn for finding this file ) https://www.cia.gov/readingroom/docs/DOC_0000500640.pdf
-

-
Now that we have covered this, lets talk about what could its RCS be?
Answer is we dont know…
Information regarding to RAM is very classified, and we cannot pinpoint its performance.
However what we have in hand a way to be able to compare the geometric stealth capabilities between different aircrafts.
This is done with the help of RCS simulations using variety of softwares.
We have to consider the fact RCS simulations should NOT be taken as real RCS, as we cant find out the RAM performance. It should only be used to compare to other jets RCS simulation under same conditions and quality of model.
Su - 57 RCS simulations :-
-
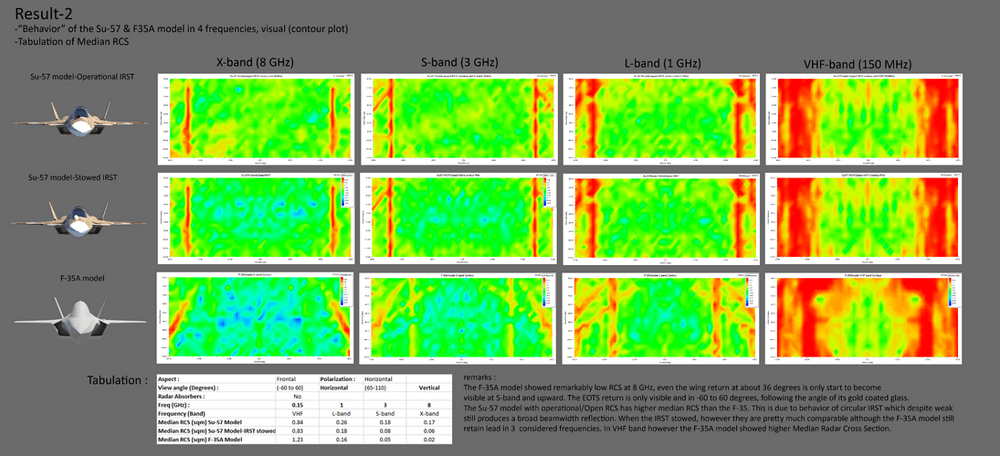
Stealthflanker’s RCS simulations
-

-
Pros
- Considers IRST with a baseline RAM
- Results across a lot of bands
- A lot of comparable aircrafts
- Considers cooling vents with a baseline RAM
-
Cons
- Does not consider variable intakes
- Low poly model
-
APA’s RCS simulation
A Preliminary Assessment of Specular Radar Cross Section Performance in the Sukhoi T-50 Prototype -
Pros
- Full 360 coverage simulation
- Results across multiple bands
- Good explanation on the working of the simulation
-
Cons
- Not a lot of aircrafts to compare to ( Only J-20 have been done in the same way)
- Uses PEA for intakes
- Doesn’t consider radar blockers/variable intakes
- Po Facets does not consider creeping wave returns
- Used older T-50 airframe, which likely didn’t have any sensor bumps
- Low poly model
-
101 RCS simulation
Su-57 Radar scattering simulation – Aircraft 101 -
Pros
- A lot of comparable aircrafts
- Good explanation on the working of simulation
- Considers FSS radomes
-
Cons
- Low poly model
- Does not consider a baseline RAM coated IRST or IGV
- Does not consider variable intakes
- DIRCM taken as fully reflective, while they are most probably mostly transparent
Out of all of these, stealthflanker’s simulations seems to be most accurate. According to his simulations, Su-57 Frontal RCS is similar to F-35, when its IRST is rotated backwards. However when using its IRST, its RCS increases significantly.
Overall, geometrically, Su-57 has solid stealth capabilities.
Su-57E
Spoiler
Currently, Algeria is the only confirmed customer of Su-57E
As of writing this, 2 Su-57E has been delivered, but pictures are not available yet
Su-57E are downgraded, and meant to be with Izdeliye 177/177S Engines instead of Al-51.
However, there is, as of now, 1 interesting detail about this variant
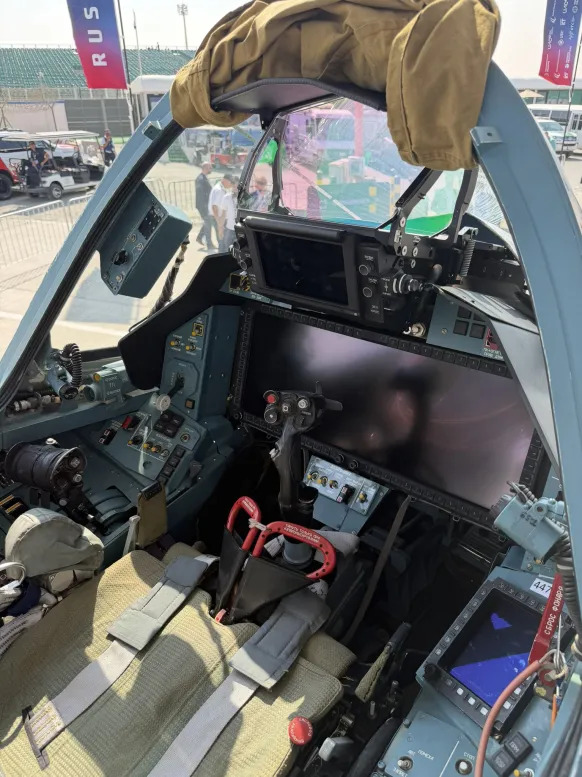

Mainly the Widescreen MFD and new HUD
Flat nozzles are also available for export
Su-57M
Spoiler
As of May 2025, a new Su-57 has reportedly went into production, the Su-57 M1. This is supposed to be Phase II
Info on this variant is not a lot, but i will list down what we know as of now, and edit as a much more comprehensive summary once enough information on it is known
-
It will have the long awaited Al-51 engines with the flat nozzles
-
It will have a new Radar suite, along with new avionics. The new radar will be GaN, but its LNA (low noise amplifier) would have chinese roots (yes i am serious on this)
-
Other before known information included a new HMD instead of the usual Russian HMS (with look through capability like F-35)
-
It might have the TVC Flat nozzles shown to public in December 2024
-
the Izdeliye 810 missiles may also go into service with this jet, which is likely to be in 2026
-
new HUD
-
new small sensors along with new MAW sensors
-
formation lights (lmao)
Also note there apparently has been 2 reported variants? T-50M1 and T-50M2? idk what this is all about, But related to Su-57M1 and possibly M2?