-
Yes
-
No

Background
Spoiler
The B-36H is a further improvement of the B-36F featuring a rearranged crew compartment, the installation of the AN/APG-41A radar for the tail gun, and relocation of K system components to a pressurized compartment.
The first flight of the B-52H was on April 5th, 1952; Although it would not be until December 1952 that units would be delivered to the USAF. Production of the aircraft would end in July of 1953, with the last unit being accepted into service of September of the same year. A total of 83 B-36H’s were produced from 1952 to 1953.
64 out of 83 B-36H’s were modified into featherweight III standards; this meant that most of the crew comforts, extra tools, and defensive armament (Save for the rear turret) were stripped out of the aircraft.
The B-36H would serve as the basis for the RB-36H, B-36J, the atomically powered NB-36H, B-36H tanker, and the DB-36H Rascal testbed (all 3 of them modified from B-36H.)
There is no hard date for the phaseout of the B-36H, although it is thought they were entirely phased out by the end of 1959.
Throughout its service life it had a few incidents, such as
2/7/1953 B-36H 51-5719 Flying through cloudy weather and ran low on fuel, crew bailed over England.
2/12/1953 B-36H 51-2729 Misguided by ground control into a hill at Goosebay, destroyed aircraft and killed two of crew members.
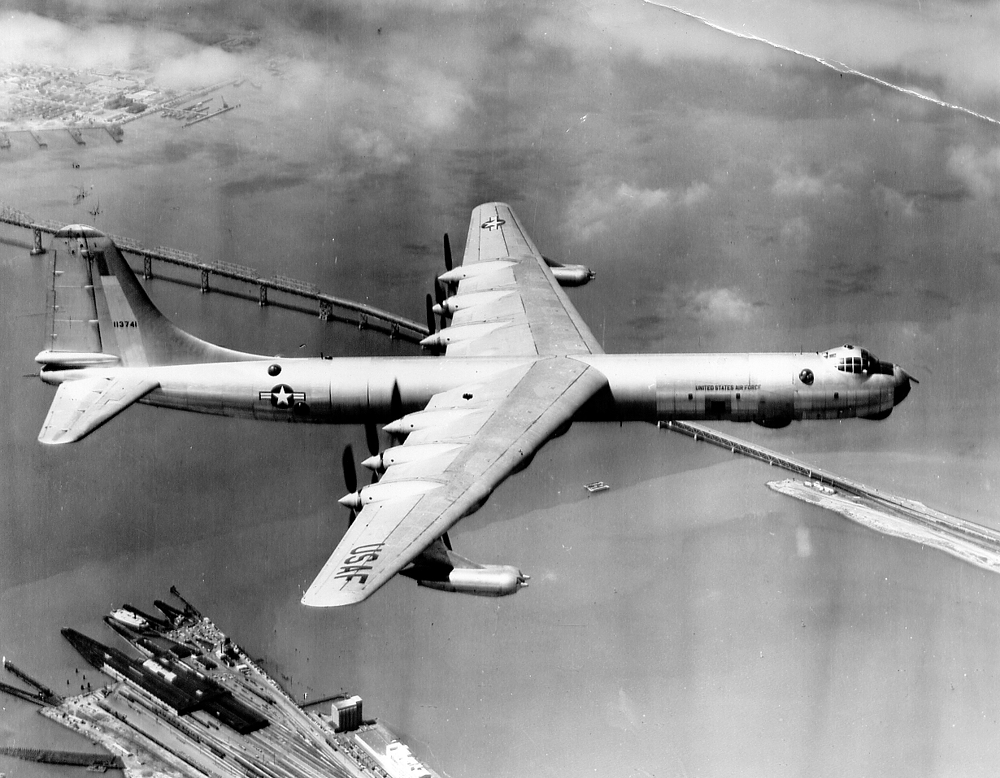
6/7/1957 B-36H 51-5741 badly damaged during flight through thunderstorm, stripped of parts and used for firefighting practice.
Technical Data
Specifications
Crew - 15
Length 49.4 m
Height - 14.3 m
Wingspan - 70.1 m
Empty Weight - 76,424 kg
Gross Weight - 115,167 kg
Max Takeoff Weight - 167,829 kg
Powerplant A - 6 x Pratt & Whitney Wasp Major R-4360-53 Pusher Prop Radial Engines (2,800 kW each)
Powerplant B - 4 x General Electric J47-GE-19 Turbojet Engines (23 kN dry)
Takeoff Run - 1,216 m at Sea Level.
Rate of climb - 4.67 m/s Standard. 10.46 m/s Emergency Power.
Cruising Speed - 378 km/h
Max Speed - 672 km/h at 11,308 m
Service Ceiling - 14,082 m
Range - 5,473 km
Armament
Up to 72,000 lb (32,659 kg) of Bombs Standard, 86,000 lb (39009 kg) Overload.
Mk-4 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-5 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-6 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-8 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-14 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-17 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-18 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-21 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-36 Nuclear Bombs.
Mk-39 Nuclear Bombs.
AN-M30A1 100 lb Bombs.
M88 220 Lb Bombs.
AN-M57A1 250 lb Bombs.
AN-MK53 Mod.1 325 lb Depth Charge Bombs.
AN-MK54 Mod.1 350 lb Depth Charge Bombs.
AN-M57A1 250 lb Bombs.
132 x AN-M64A1500 lb Bombs.
132 x AN-M85A2 500lb Bombs.
129 x MK-82 500 lb Bombs.
48 x M117 750 lb Bombs.
72 x AN-M65A1 1,000 lb Bombs.
72 x AN-M59A1 1,000 lb Bombs.
72 x AN-MK33 1,000 lb Bombs
Mk 36 1000 lb Sea Mine Bombs.
Mk 36 Mod 1 1000 lb Sea Mine Bombs.
MK26 Mod 1 1000 lb Sea Mine Bombs.
44 x AN-MK1 1,600 lb Bombs.
MK 25 2,000 lb Sea Mine Bombs.
Mk 10 Mod.9 2,000 lb Sea Mine Bombs.
28 x AN-M66A2 2,000 lb Bombs.
12 x AN-M56 4,000 lb Bombs.
4 x T-10 12,000 lb Bombs.
3 x M110 22,000 lb Bombs.
2 × T-12 43,000 lb Bombs.
(2 x 1) x 8 M24A1 20mm Cannons in Retractable Mounts. (16 Cannons Total) (92,000 Ammunition Total)
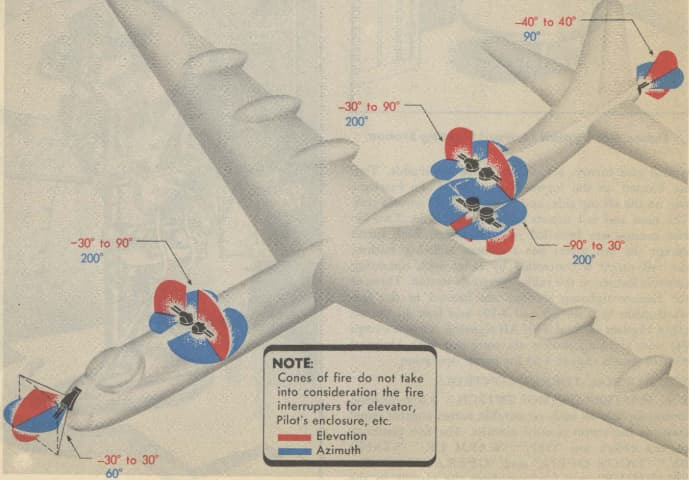
Avionics
A-7 Chaff Dispenser
K-3A Bombing and Navigational Radar
Y-3A Optical and Radar Sight
AN/APG-41A Radar (Tail Gun)
AN/APX-6 IFF
Images
Sources
Spoiler
Marcelle S. Knaack’s Encyclopedia of U.S. Air Force Aircraft and Missile Systems Volume II, Post-World War II Bombers 1945-1973 (Book)
Warbird Tech Series Vol.24 (PDF)
SAC 3-DEC-1951 B-36H Peacemaker (PDF)



