- Yes
- No
History
The AH-64 Apache, introduced in 1986, served as a backbone of the U.S. Army Aviation. It was first used in combat in 1989 and has seen action in conflicts in Iraq, Bosnia, Kosovo and Afghanistan. While there were many combat losses along the way, its superior performance has been clearly demonstrated in the combat.
Thus, Apache has been steadily improved over the years. The AH-64D was the most famous of these, with the iconic Longbow radar which provides improved target acquisition capabilities.
The current variant AH-64E is direct evolution of the AH-64D. It was started as AH-64D Block III, later renamed to AH-64E for avoid confusion with the AH-64D Block II. The Apache Project Office christened the AH-64E as “Guardian”, because it functions as a safeguard for soldiers on the ground.
Currently the U.S. Army operates 700 AH-64E, which is about 90% of the U.S. Army’s attack helicopter fleet.
Design
AH-64E v6 is the latest version of Apache. While most of the AH-64D’s basic structure has been retained, a number of internal improvements have been made.
Airframe and Engine

T700-GE-701C and T700-GE-701D
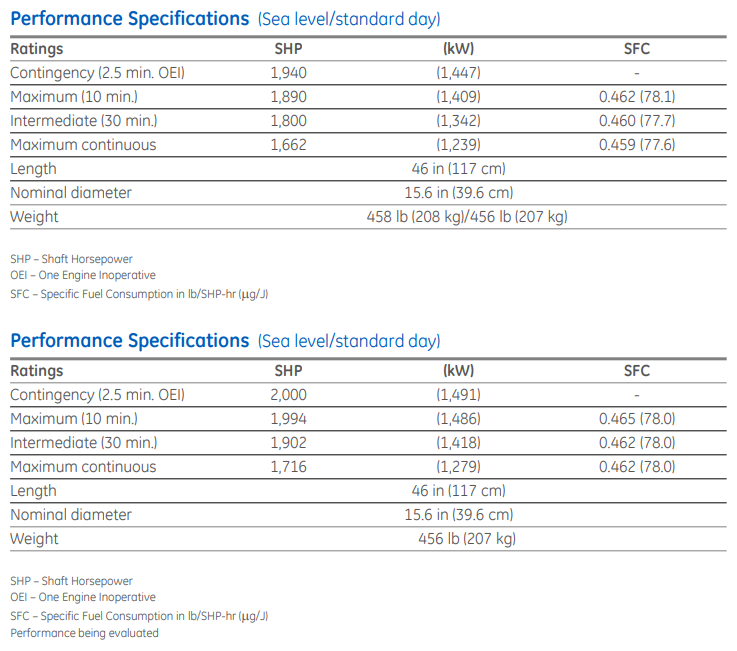
The AH-64E uses slightly more powerful T700-GE-701D engines with upgraded face gear transmission to accommodate more power.
Avionics
The AH-64E’s AN/APG-78 fire control radar has been upgraded in version 6. The target detection range is doubled to 16 km, and it could detect UAVs better.
Addition to the range expansion, v6 also added several FCR modes like single target track for air and ground targets.
The RWR was replaced by the AN/APR-39(E)V2, which can also detect C-D bands.
Armament and countermeasures
The AH-64E retains weapon capabilities of the legacy Apaches, with some additions.
In 2023, the Lockheed Martin integrated Spike NLOS missile to the AH-64E v6 in Yuma Proving Grounds and performed 8 live firings. Currently the Spike NLOS is operational on the U.S. AH-64E.
The Spike NLOS has a much longer range than previous Spikes, but midcourse guidance via datalink is required to attack targets more than 8 kilometers away. However the datalink capability of air-to-ground missiles is currently not implemented in-game, the launch range against moving targets will be lot limited.
This would be a reasonable enough, as it allows FNF missiles to U.S. helicopters without significant game balance problems.
The AH-64E features improved survivability by adding Common Infrared Countermeasures (CIRCM) on its wingtip. It is a DIRCM system, which works in conjunction with AN/AAR-57 CMWS.
It takes place of the wingtip air-to-air Stinger (ATAS), so the AH-64E v6 added ATAS provisions on the outboard stub wing station. This enables four ATAS with wingtip DIRCM.

Besides DIRCM, AH-64E carries three M130 chaff/flare dispensers on its tail boom.
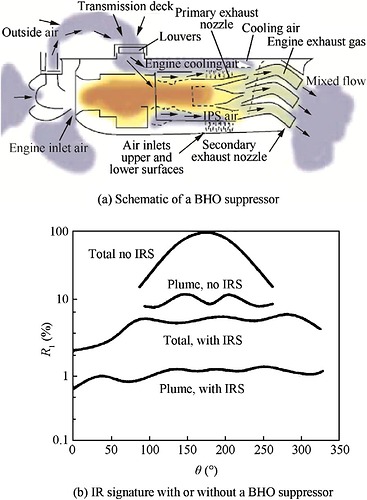
Just like older Apaches, the AH-64E has built-in Black Hole Ocarina infrared suppressors to reduce IR signature. An additional IR deflector directs the exhaust gas upward to enhance BHO’s effectiveness.
Specifications
Crew: 2 (pilot, co-pilot/gunner)
Length: 48.16 ft (14.68 m)
Rotor diameter: 48 ft (14.63 m)
Height: 15.49 ft (4.72 m)
Weight:
- Gross: 15,075 lb (6,838 kg)
- Maximum operating: 23,000 lb (10,432 kg)
Powerplant: T700-GE-701D
- Thrust:
- Contingency: 2,000 shp
- Maximum: 1,994 shp
- Intermediate: 1,902 shp
- Maximum continuous: 1,716 shp
Performances:
- Maximum rate of climb: 2,800+ ft/m (14.22+ m/s)
- Maximum level flight speed: 150+ kn (277.8 km/h)
- Service ceiling: 20,000 ft (6,096 m)
Armament:
- Hardpoints: 4
- Gun: 30 mm M230 chain gun (1,200 rounds)
- Air-to-air missiles: 4× AIM-92 ATAS
- Air-to-ground missiles:
- 16× AGM-114R Hellfire II
- 16× AGM-179 JAGM
- 16× Spike NLOS
- Mass: 74.8 kg
- Guidance: IR
- Rockets:
- 76× Hydra 70
- 76× APKWS II
Avionics:
- Radar: AN/APG-78 Longbow
- RWR: AN/APR-39E(V)2
- Band: C-M
- ESM: AN/APR-48A RFI
- FLIR: M-TADS/PNVS
- LWR: AN/AVR-2B
- MAWS: AN/AAR-57 CMWS
Countermeasures:
- Chaff/Flares: 3× M130 (90 total)
- DIRCM: 2× CIRCM (each on wingtip)
- HIRSS: BHO + IR deflectors
Sources
- AH-64 Apache
- AN/AAR-57 Common Missile Warning System (CMWS) - BAE Systems
- AN/APR-39 Digital Radar Warning Receiver Family
- AUSA 2019: AH-64E APACHE Sensor Suite Upgrades
- Apache Capability Enhancements (ACE) Industry Days by Joseph Herman
- Army aviators testing next generation air-to-ground missile - Army.mil
- CIRCM - Common Infrared Countermeasures - Northrop Grumman | Northrop Grumman
- CIRCM - 5th Generation IRCM Technology for Unparalleled Warfighter Protection
- Common Infrared Countermeasures (CIRCM)
- DVIDS - News - Spike missile integrated into Apache helicopter at Yuma Proving Ground
- DVIDS - Images - Task Force Dragon Erbil Iraq [Image 2 of 11]
- DVIDS - Images - U.S. Army AH-64E Apaches conduct refueling operations [Image 5 of 15]
- Infrared Signature Suppression of Helicopter Engine Duct Based on Conceal and Camouflage by Shripad P. Mahulikar
- Joint Air-to-Ground Missile (JAGM)
- Major protector of aircraft achieves Initial Operational Capability - PEO IEW&S
- NT Spike - Teal Group
- Progress in helicopter infrared signature suppression by Zhang Jingzhou, Pan Chengxiong and Shan Yong
- Rafael to Showcase Breakthrough Laser Defense, Air Defense, and Precision Strike Systems at AUSA 2024
- Successful Live Fire Demo Clears Path for Spike NLOS Airworthiness Release onto U.S. Apache - Lockheed Martin
- The Modernized AH-64 Apache
- U.S. Army reveals details of AH-64E Apache ‘Version 6’ update
- United States Army Aviation Digest Volume 25